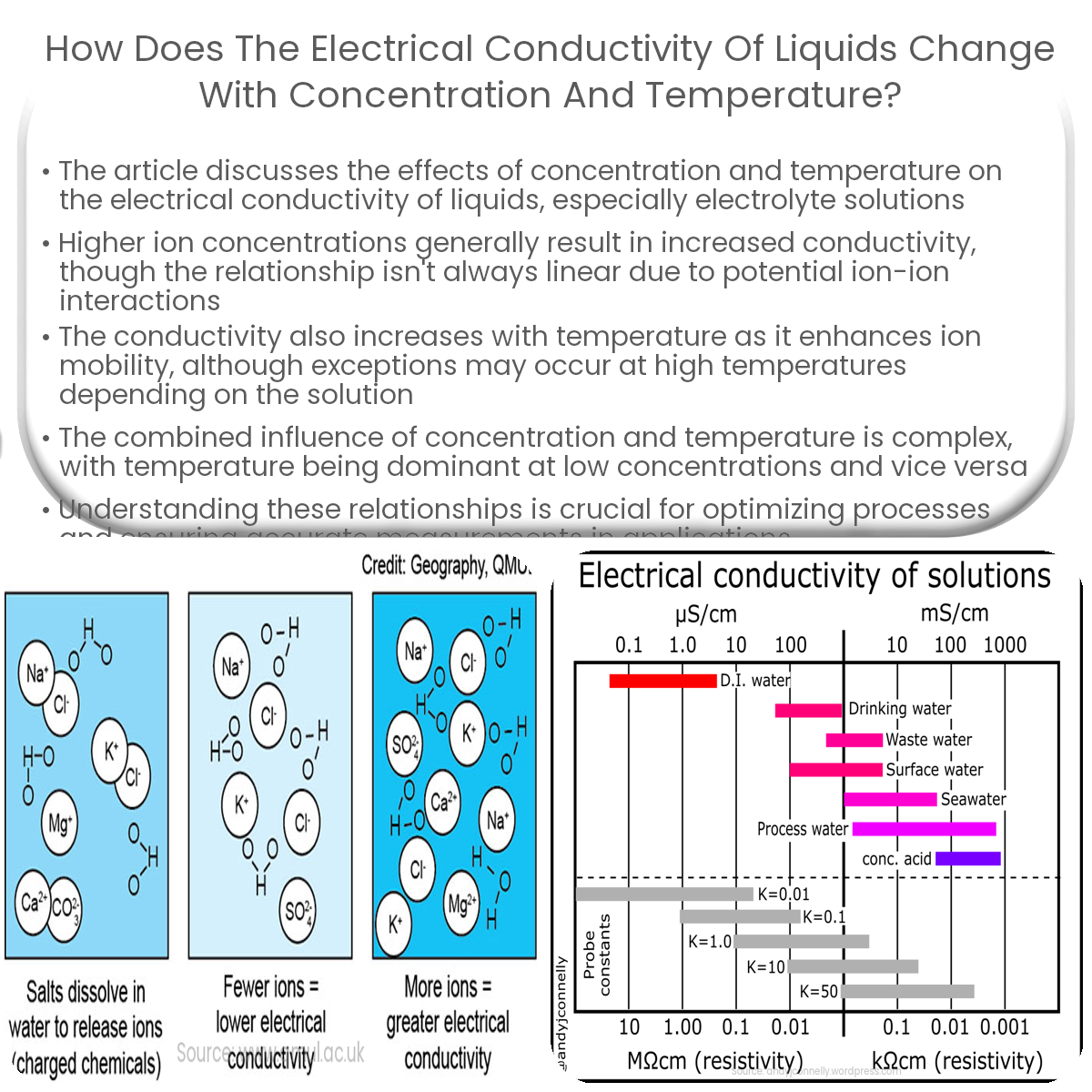
Electrical conductivity of liquids changes with concentration (more ions) and temperature (higher ion mobility), but the relationship is complex.
Electrical Conductivity of Liquids: Effects of Concentration and Temperature
Electrical conductivity in liquids, particularly electrolyte solutions, is an important property for various applications in science and technology. The electrical conductivity of a liquid is influenced by multiple factors, including concentration and temperature. In this article, we will discuss how these factors impact the conductivity of liquids.
Effect of Concentration
The electrical conductivity of an electrolyte solution depends on the concentration of ions present in the solution. As the concentration of ions increases, the number of charge carriers available to conduct electricity also increases. This generally leads to a higher electrical conductivity. However, it’s important to note that the relationship between concentration and conductivity is not always linear.
In dilute solutions, the increase in conductivity with concentration is more pronounced as there are fewer ions present to begin with. However, as the concentration increases further, the rate of increase in conductivity starts to decline. This is due to the increased probability of ion-ion interactions, which can hinder the mobility of charge carriers.
Effect of Temperature
Temperature also plays a significant role in determining the electrical conductivity of a liquid. As the temperature of a solution increases, the kinetic energy of the ions increases, leading to higher mobility and, consequently, higher electrical conductivity. This is generally observed as a linear relationship between temperature and conductivity for most electrolyte solutions.
However, this relationship can deviate from linearity at higher temperatures, depending on the nature of the electrolyte and the solvent. For instance, the conductivity of some solutions may decrease with increasing temperature due to a decrease in solubility or the formation of complexes.
Combined Effects of Concentration and Temperature
The combined effects of concentration and temperature on the electrical conductivity of liquids can be complex. At low concentrations and high temperatures, the conductivity is primarily dominated by the temperature effect. Conversely, at high concentrations and low temperatures, the concentration effect becomes more significant.
In practical applications, understanding the relationship between concentration, temperature, and conductivity is crucial for optimizing processes and ensuring accurate measurements. It’s essential to consider both factors when characterizing the electrical properties of liquids and designing systems that rely on these properties.