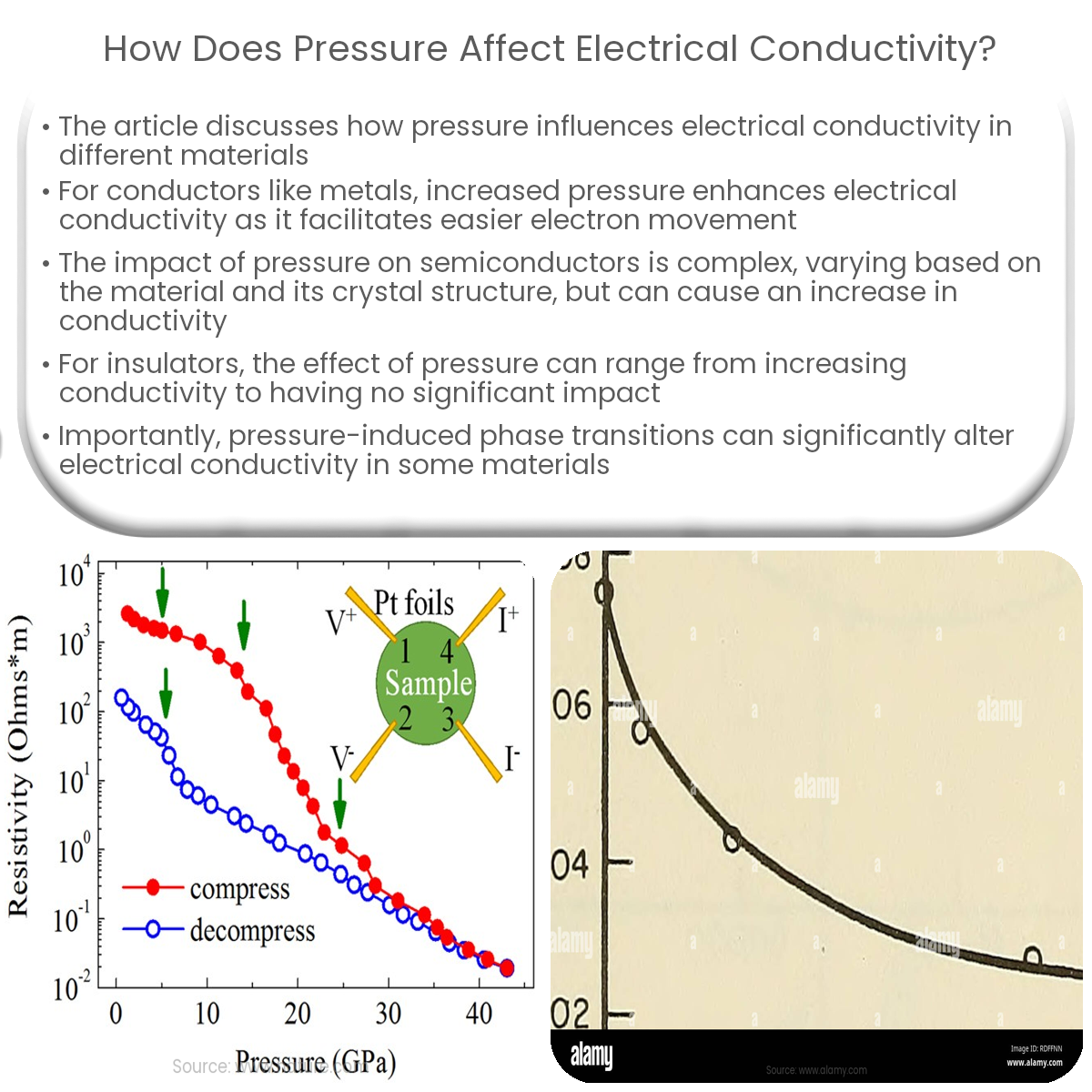
Pressure affects conductivity differently in conductors, semiconductors, and insulators, altering atomic distances, band structures, and energy gaps.
Pressure and Electrical Conductivity
Electrical conductivity is influenced by various factors, including temperature, pressure, and impurities. This article focuses on understanding how pressure affects electrical conductivity in different materials.
Effect of Pressure on Conductors
For conductors, such as metals, increasing pressure generally results in an increase in electrical conductivity. The reason is that higher pressure brings the atoms in a material closer together, thereby reducing the average distance between atoms and facilitating easier electron movement. This leads to an increase in the material’s conductivity.
Effect of Pressure on Semiconductors
In semiconductors, the effect of pressure on electrical conductivity is more complex. The impact of pressure on conductivity in semiconductors depends on the specific material and its crystal structure. For example, silicon and germanium, two common semiconductors, exhibit an increase in electrical conductivity under high pressure. This is due to changes in their band structures, which alter the energy gap between the valence and conduction bands, thus affecting the conductivity.
Effect of Pressure on Insulators
For insulators, the effect of pressure on electrical conductivity can vary depending on the material. In some cases, pressure can cause insulators to become more conductive by reducing the energy gap between the valence and conduction bands. In other cases, pressure may not have a significant impact on the electrical conductivity of insulators.
Pressure-induced Phase Transitions and Conductivity
It is important to note that pressure can also cause phase transitions in certain materials, which can significantly affect their electrical conductivity. When a material undergoes a phase transition due to pressure, its crystal structure and electronic properties can change dramatically, resulting in a marked change in electrical conductivity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pressure can have varying effects on electrical conductivity depending on the type of material being examined. For conductors, increased pressure typically leads to an increase in conductivity. In semiconductors and insulators, the effect of pressure on conductivity is more complex and depends on the specific material and its properties. Understanding the relationship between pressure and electrical conductivity is essential for designing and optimizing electrical systems and devices that operate under varying pressure conditions.