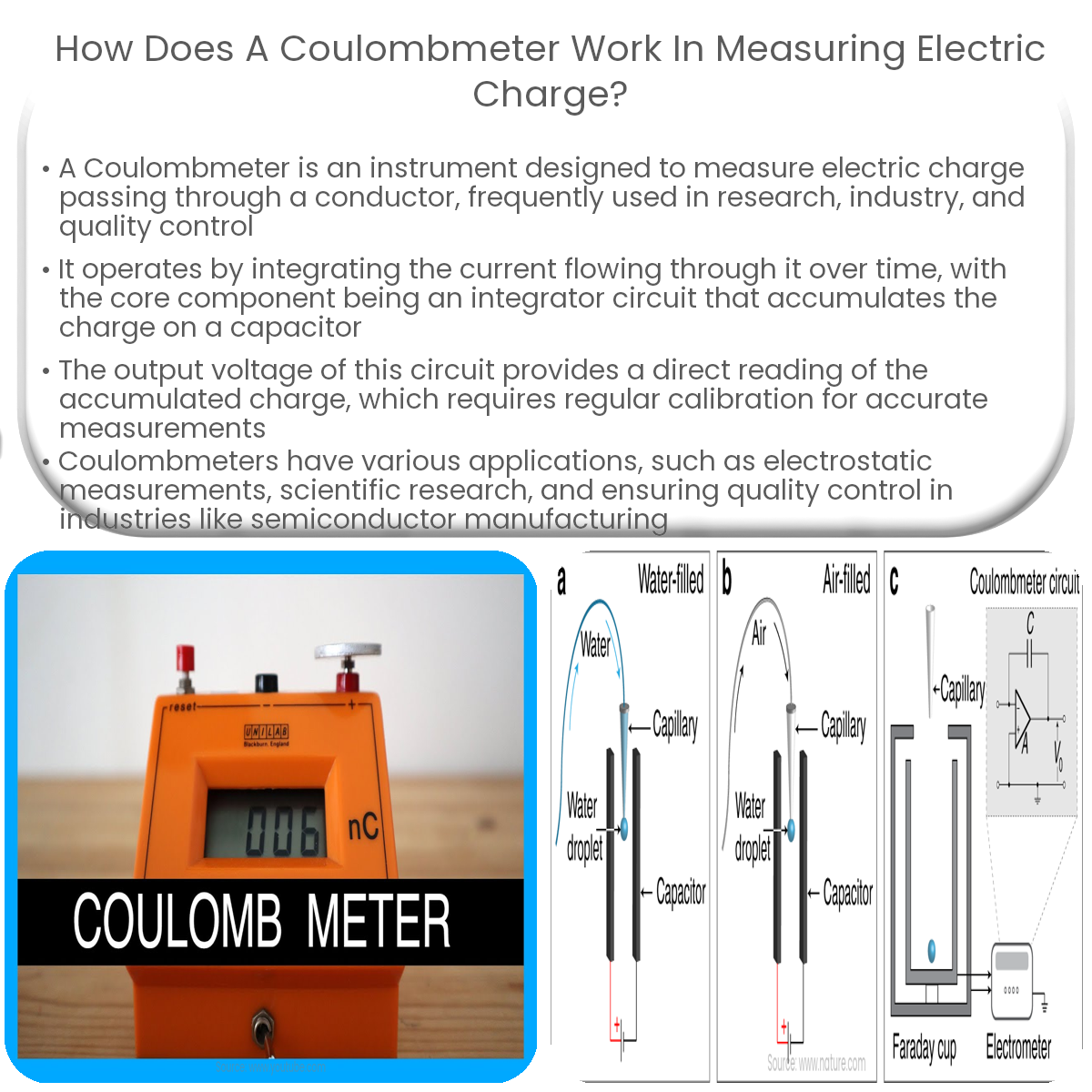
A Coulombmeter measures electric charge by integrating current over time using an integrator circuit with an op-amp and a capacitor.
Understanding Coulombmeters
A Coulombmeter is an electronic instrument designed to measure the electric charge passing through a conductor or circuit element. This device is commonly used in various applications, including research, industry, and quality control. To understand how a Coulombmeter works, it is essential to comprehend the fundamental principles of electric charge measurement.
Measuring Electric Charge
Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. The unit of charge is the Coulomb (C), and the flow of charge is called electric current, measured in amperes (A). The relationship between charge and current is given by the equation:
Q = I × t
where Q is the charge, I is the current, and t is the time over which the current flows.
Operating Principle of a Coulombmeter
A Coulombmeter works by integrating the current flowing through the device over time, effectively converting the time-domain information into charge-domain information. The core component of a Coulombmeter is an integrator circuit, typically implemented using an operational amplifier (op-amp) and a capacitor.
As the electric current passes through the Coulombmeter, the integrator circuit accumulates the charge on the capacitor. The voltage across the capacitor is directly proportional to the accumulated charge, according to the equation:
Q = C × V
where Q is the charge, C is the capacitance of the capacitor, and V is the voltage across the capacitor.
Reading and Calibration
The output voltage of the integrator circuit is measured and scaled to provide a direct reading of the accumulated charge. This measurement can be displayed on a digital or analog display, or it can be transmitted to other electronic devices for further processing and analysis.
For accurate measurements, a Coulombmeter must be calibrated regularly. Calibration involves applying a known charge to the device and adjusting the scaling factor or gain of the measurement circuitry to ensure an accurate reading.
Applications of Coulombmeters
- Electrostatic Measurements: Coulombmeters are commonly used to measure the charge on surfaces or objects in electrostatic applications, such as studying electrostatic discharge (ESD) or monitoring charge accumulation in manufacturing processes.
- Research and Development: In scientific research, Coulombmeters can be used to study the behavior of charged particles or to investigate electric properties of materials.
- Quality Control: In industries like semiconductor manufacturing or electronics assembly, Coulombmeters can be used for quality control purposes, ensuring that charged components or devices are within specified tolerances.