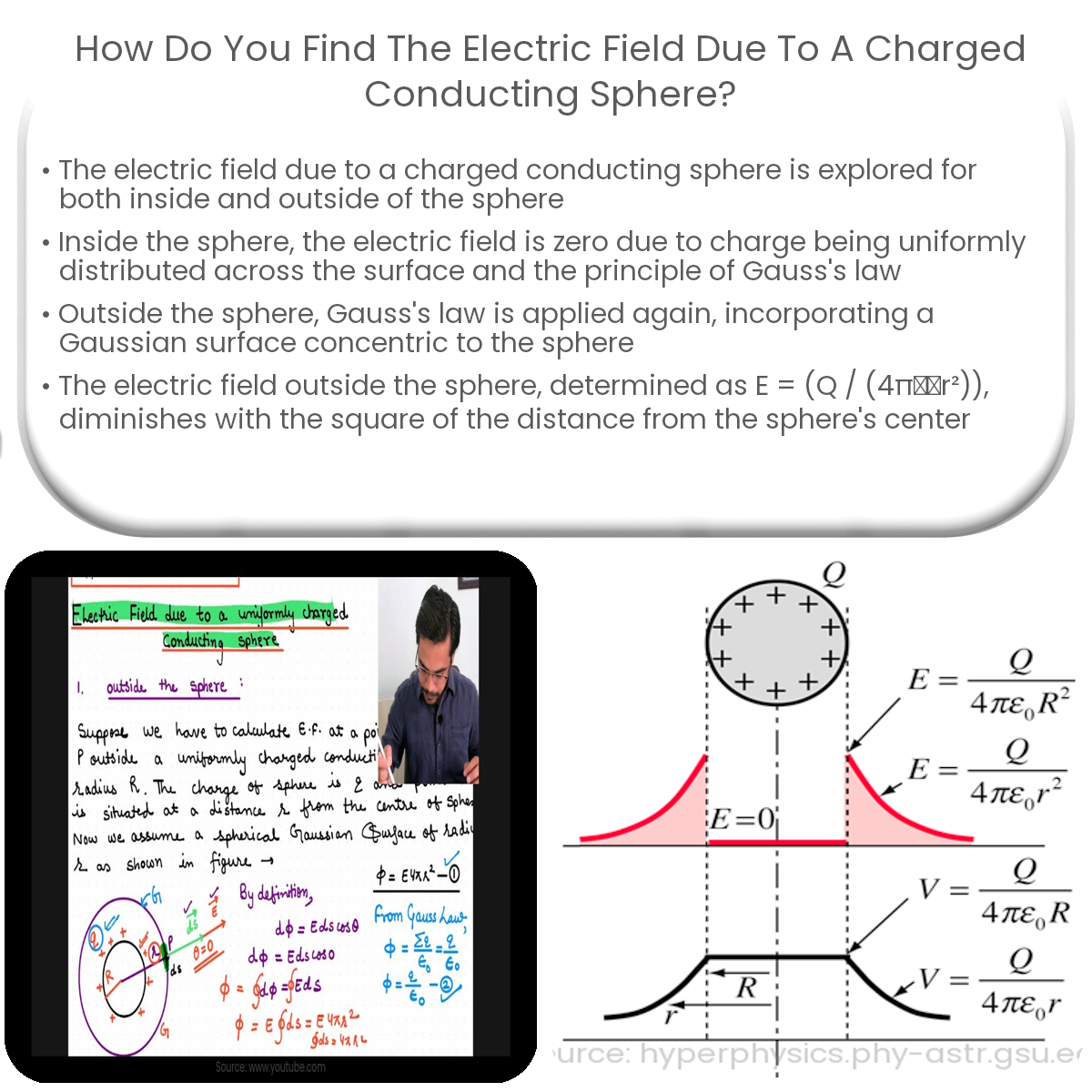
Inside the sphere, the electric field is zero. Outside, it’s calculated as E = (Q / (4πε₀r²)), where Q is charge, ε₀ is vacuum permittivity, and r is radius.
Finding the Electric Field Due to a Charged Conducting Sphere
The electric field due to a charged conducting sphere is an essential concept in electromagnetism. To find the electric field, we need to consider two different cases: the electric field inside the sphere and the electric field outside the sphere.
1. Electric Field Inside the Sphere
In the case of a conducting sphere, the electric charge is distributed uniformly over the surface of the sphere. Due to the symmetry of the sphere and the fact that it is a conductor, the electric field inside the sphere is zero. This phenomenon is a direct result of Gauss’s law, which states that the net electric flux through a closed surface is proportional to the enclosed electric charge.
2. Electric Field Outside the Sphere
To find the electric field outside the sphere, we can use Gauss’s law as well. First, we need to consider a Gaussian surface in the shape of a concentric sphere with the same center as the conducting sphere and a radius larger than the conducting sphere’s radius. Since the electric field is radially symmetric, it is constant on the Gaussian surface.
According to Gauss’s law, the total electric flux through the Gaussian surface is equal to the enclosed charge divided by the vacuum permittivity (ε₀):
Φ = Q / ε₀
Next, we calculate the electric flux through the Gaussian surface:
Φ = E * A
Where E is the electric field and A is the surface area of the Gaussian surface, which is given by A = 4πr², with r being the radius of the Gaussian surface.
Combining the two equations and solving for the electric field E, we get:
E = (Q / ε₀) / (4πr²)
Thus, the electric field due to a charged conducting sphere outside the sphere is given by:
E = (Q / (4πε₀r²))
This equation shows that the electric field outside the charged conducting sphere decreases with the square of the distance from the center of the sphere.