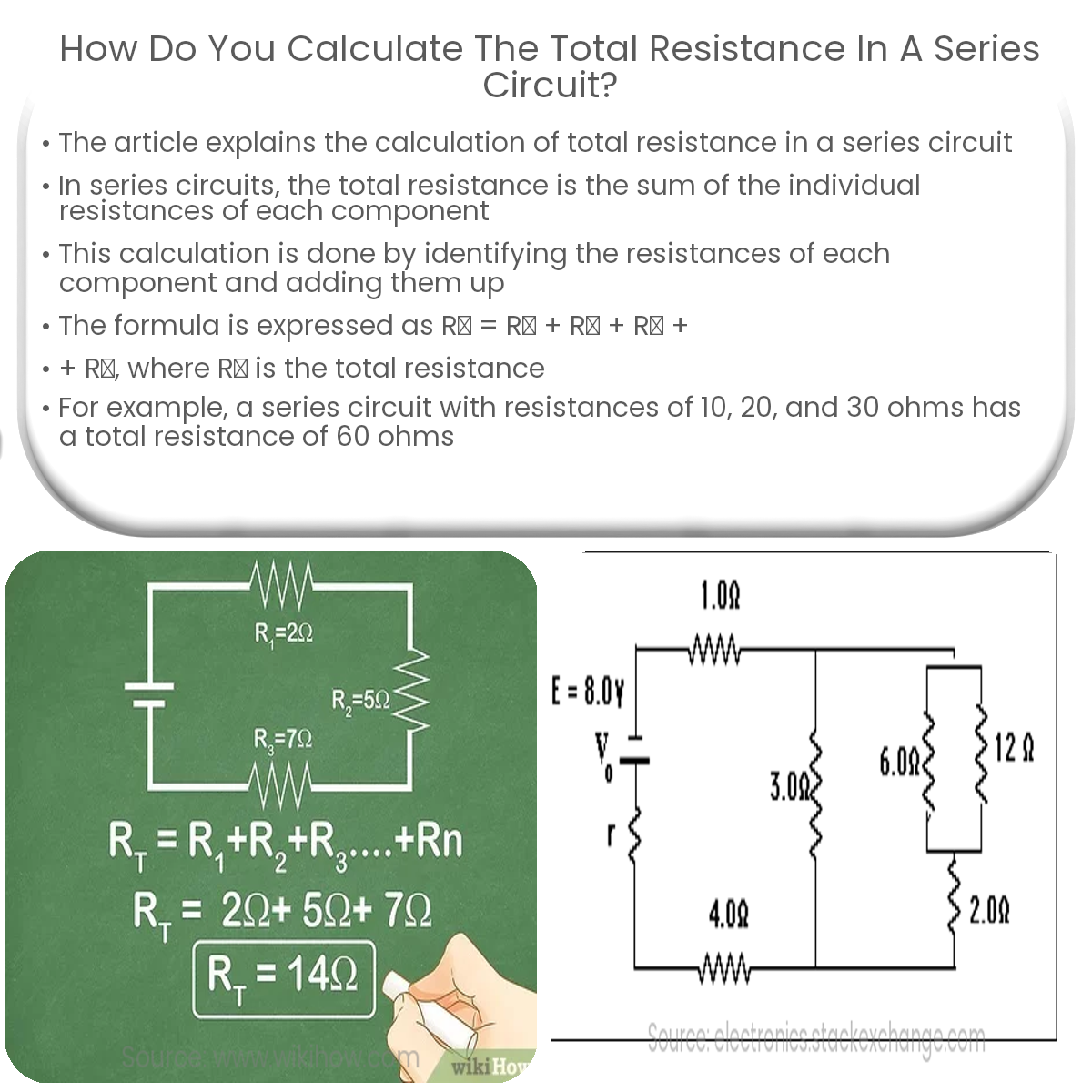
To calculate total resistance in a series circuit, add the individual resistances of all components in the circuit.
Calculating Total Resistance in a Series Circuit
In a series circuit, components are connected end-to-end in a single path, so the current flows through each component in turn. This article will explain how to calculate the total resistance in a series circuit.
Understanding Resistance in Series Circuits
When resistors are connected in series, the total resistance is equal to the sum of their individual resistances. This means that the current has to pass through each resistor, and the resistances add up to create a higher overall resistance.
Formula for Total Resistance in a Series Circuit
To calculate the total resistance in a series circuit, simply add the individual resistance values:
- Identify the resistances of each component in the circuit.
- Add the resistances together to find the total resistance.
Mathematically, the formula can be expressed as:
RT = R1 + R2 + R3 + … + Rn
Where RT is the total resistance, and R1, R2, R3, … Rn are the individual resistances of the components in the series circuit.
Example of Calculating Total Resistance in a Series Circuit
Consider a series circuit with three resistors connected in series: R1 = 10 ohms, R2 = 20 ohms, and R3 = 30 ohms. To calculate the total resistance:
- Add the individual resistances: RT = R1 + R2 + R3
- RT = 10 ohms + 20 ohms + 30 ohms
- RT = 60 ohms
The total resistance of the series circuit is 60 ohms.
Conclusion
Calculating the total resistance in a series circuit is straightforward. Simply add the individual resistances of each component to find the total resistance. This is important for understanding the overall behavior of a series circuit and how the current flows through each component.