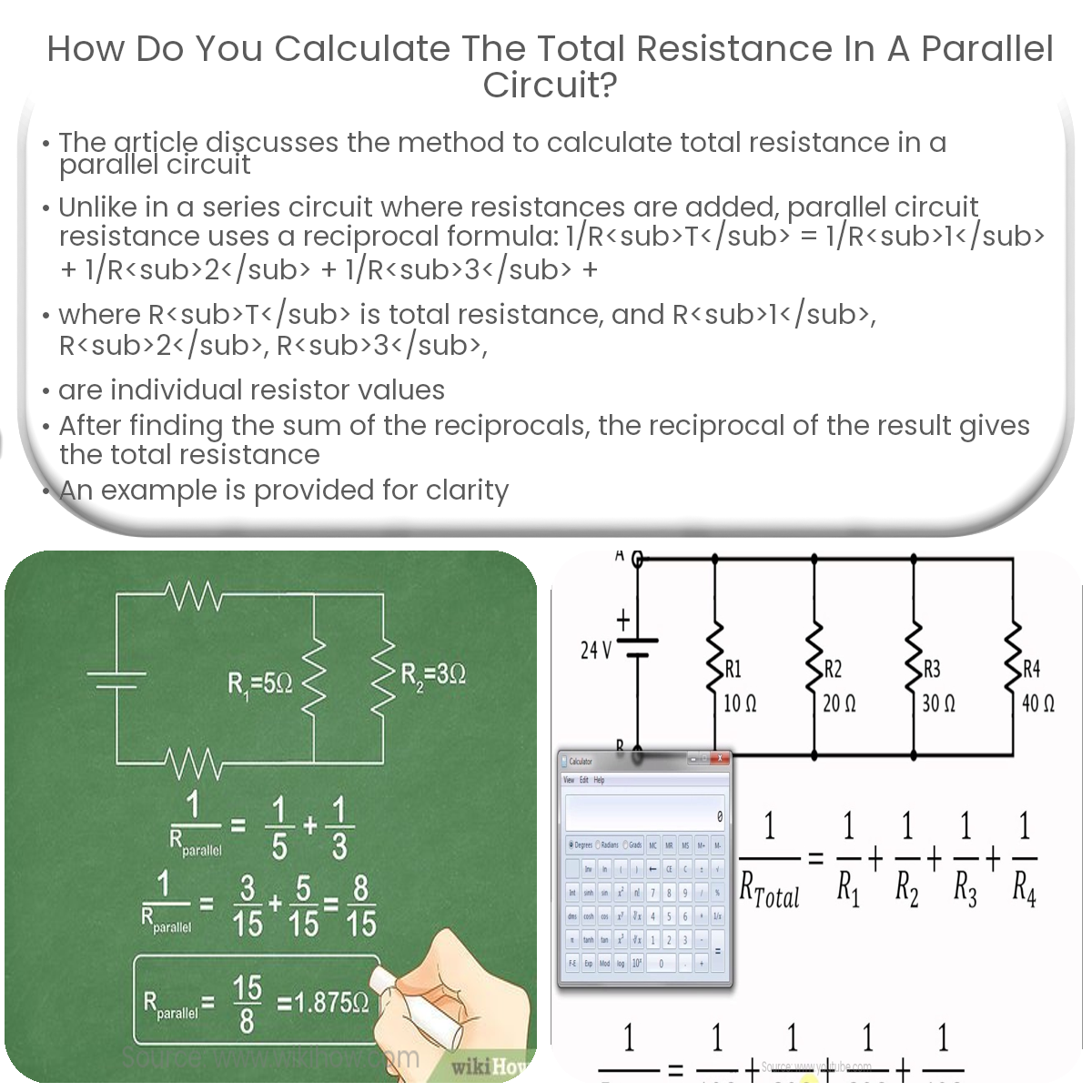
In a parallel circuit, total resistance is calculated using the formula: 1/RT = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 + … . Take the reciprocal of the sum to get RT.
Calculating Total Resistance in a Parallel Circuit
In a parallel circuit, resistors are connected in such a way that the current has multiple paths to flow through. Calculating the total resistance in a parallel circuit is different from a series circuit. This article will explain the method used to determine the total resistance of resistors in parallel.
Formula for Parallel Resistance
Unlike a series circuit, where resistances are simply added, the total resistance in a parallel circuit is calculated using the reciprocal formula:
1/RT = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 + …
Where RT is the total resistance, and R1, R2, R3, … are the individual resistor values in the circuit. After finding the sum of the reciprocals, take the reciprocal of the result to obtain the total resistance.
Example Calculation
Let’s consider a parallel circuit with three resistors, R1 = 4Ω, R2 = 6Ω, and R3 = 12Ω. We can calculate the total resistance as follows:
- Find the reciprocals of the individual resistances:
- Add the reciprocals together:
- Take the reciprocal of the sum:
1/R1 = 1/4Ω = 0.25 S
1/R2 = 1/6Ω = 0.1667 S
1/R3 = 1/12Ω = 0.0833 S
0.25 S + 0.1667 S + 0.0833 S = 0.5 S
RT = 1/0.5 S = 2Ω
The total resistance of the parallel circuit is 2Ω.
Conclusion
Calculating the total resistance in a parallel circuit involves using the reciprocal formula. Remember to find the reciprocals of individual resistances, add them together, and then take the reciprocal of the sum to obtain the total resistance.