To calculate power consumption in an electric circuit, use the formula P = VI for DC circuits or P = VI * power factor for AC circuits.
Calculating Power Consumption in Electric Circuits
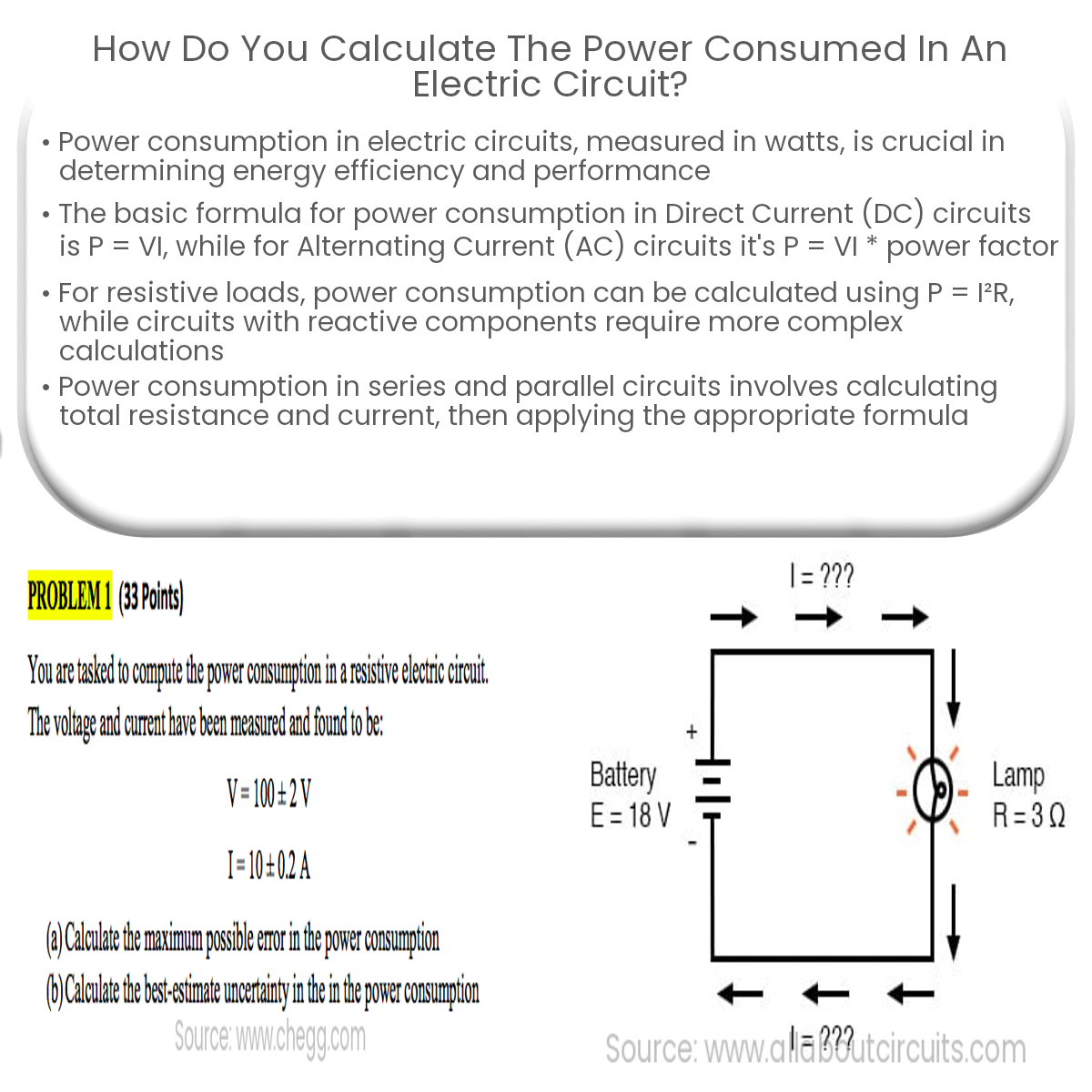
Power consumption is a critical concept in electrical engineering, as it helps determine the energy efficiency and performance of a circuit. This article will discuss the basics of power consumption in electric circuits and how to calculate it using various formulas.
Understanding Power Consumption
Power, measured in watts (W), is the rate at which electrical energy is converted into other forms of energy, such as heat or mechanical work. In an electric circuit, power consumption can be understood as the amount of energy used by the electrical components.
Basic Formulas for Power Consumption
- Direct Current (DC) Circuits: In a DC circuit, power consumption can be calculated using the formula P = VI, where P is power, V is voltage, and I is current.
- Alternating Current (AC) Circuits: In an AC circuit, the formula becomes P = VI * power factor, where the power factor is a dimensionless number ranging from 0 to 1 that represents the phase difference between voltage and current.
- Resistive Loads: For resistive loads, such as incandescent light bulbs or electric heaters, power consumption can be calculated using P = I2R, where R is the resistance of the load.
- Reactive Loads: In circuits with reactive components, such as inductors or capacitors, power consumption is more complex and involves calculating the real and reactive power components.
Calculating Power Consumption in Series and Parallel Circuits
- Series Circuits: In a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of all resistances. Calculate the total current using Ohm’s Law (I = V/R) and then use the formula P = I2R for each individual component to find their power consumption.
- Parallel Circuits: In a parallel circuit, the total resistance can be calculated using the formula 1/RT = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + … + 1/Rn. Determine the current for each component using Ohm’s Law and then calculate their power consumption using the P = I2R formula.
In conclusion, calculating power consumption in electric circuits is essential for understanding energy efficiency and performance. By employing the appropriate formulas and understanding the differences between DC and AC circuits, as well as series and parallel circuits, you can effectively determine the power consumed by various electrical components.