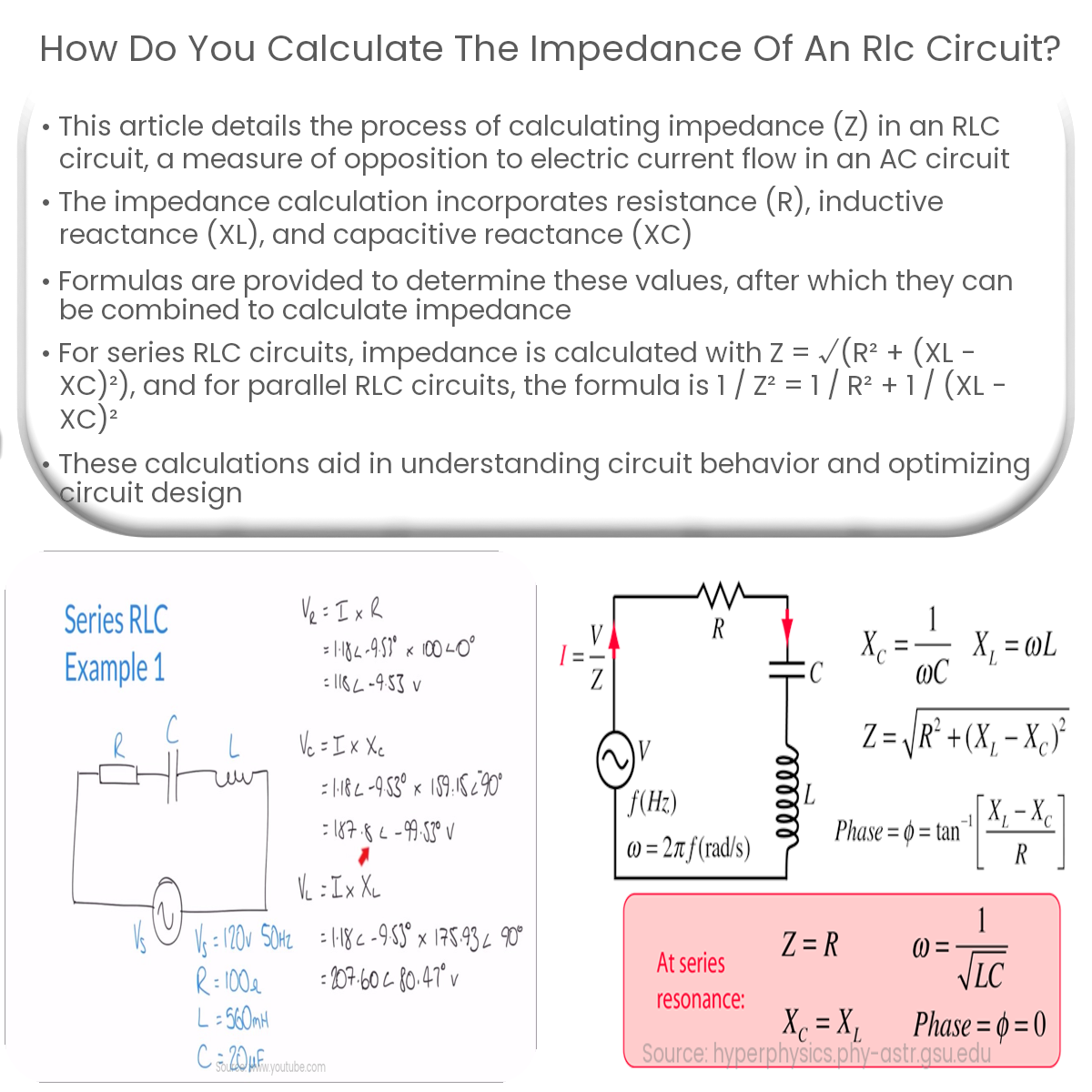
Calculate impedance in a series RLC circuit: Z = √(R² + (XL – XC)²) and in a parallel RLC circuit: 1 / Z² = 1 / R² + 1 / (XL – XC)².
Calculating the Impedance of an RLC Circuit
Impedance, denoted as Z, is a measure of the opposition to the flow of electric current in an alternating current (AC) circuit. It is a complex quantity that takes into account resistance (R), inductive reactance (XL), and capacitive reactance (XC) in an RLC circuit. To calculate the impedance of an RLC circuit, you need to determine the values of these three components and then combine them appropriately. This article will walk you through the process step by step.
Finding Resistance, Inductive Reactance, and Capacitive Reactance
In an RLC circuit, there are three main components:
- Resistance (R): The opposition to the flow of direct current (DC), measured in ohms (Ω). It is determined by the resistors in the circuit.
- Inductive Reactance (XL): The opposition to the flow of AC caused by the presence of an inductor, measured in ohms (Ω). It is calculated using the formula XL = 2πfL, where f is the frequency of the AC signal in hertz (Hz), and L is the inductance of the inductor in henries (H).
- Capacitive Reactance (XC): The opposition to the flow of AC caused by the presence of a capacitor, measured in ohms (Ω). It is calculated using the formula XC = 1 / (2πfC), where f is the frequency of the AC signal in hertz (Hz), and C is the capacitance of the capacitor in farads (F).
Once you have determined the values of R, XL, and XC, you can calculate the impedance of the RLC circuit.
Calculating the Impedance
Impedance in an RLC circuit is the vector sum of resistance, inductive reactance, and capacitive reactance. In a series RLC circuit, the impedance is calculated using the following formula:
Z = √(R² + (XL – XC)²)
In a parallel RLC circuit, the impedance is calculated using the following formula:
1 / Z² = 1 / R² + 1 / (XL – XC)²
Once you have computed the impedance, you can represent it in polar form as Z = |Z|∠θ, where |Z| is the magnitude of the impedance, and θ is the phase angle. The phase angle can be calculated using the following formula:
θ = arctan((XL – XC) / R)
By calculating the impedance of an RLC circuit, you can better understand the behavior of the circuit and design it more effectively to meet specific requirements.