To calculate power, use P = W/t for mechanical power, P = V × I for electrical power, and P = τ × ω for rotational power, based on the system type.
Calculating Power: An Overview
Power is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, representing the rate at which energy is transferred or converted. Understanding how to calculate power is essential for analyzing and designing various systems, from electrical circuits to mechanical devices. This article provides an overview of the different methods to calculate power based on the context and the type of energy involved.
1. Mechanical Power
Mechanical power is the rate at which work is done or the energy is transferred in a mechanical system. It can be calculated using the following formula:
P = W / t
- P: Power (measured in watts, W)
- W: Work done or energy transferred (measured in joules, J)
- t: Time taken (measured in seconds, s)
For a system involving a constant force and constant velocity, the mechanical power can also be calculated using the following formula:
P = F × d / t
- F: Force (measured in newtons, N)
- d: Distance (measured in meters, m)
2. Electrical Power
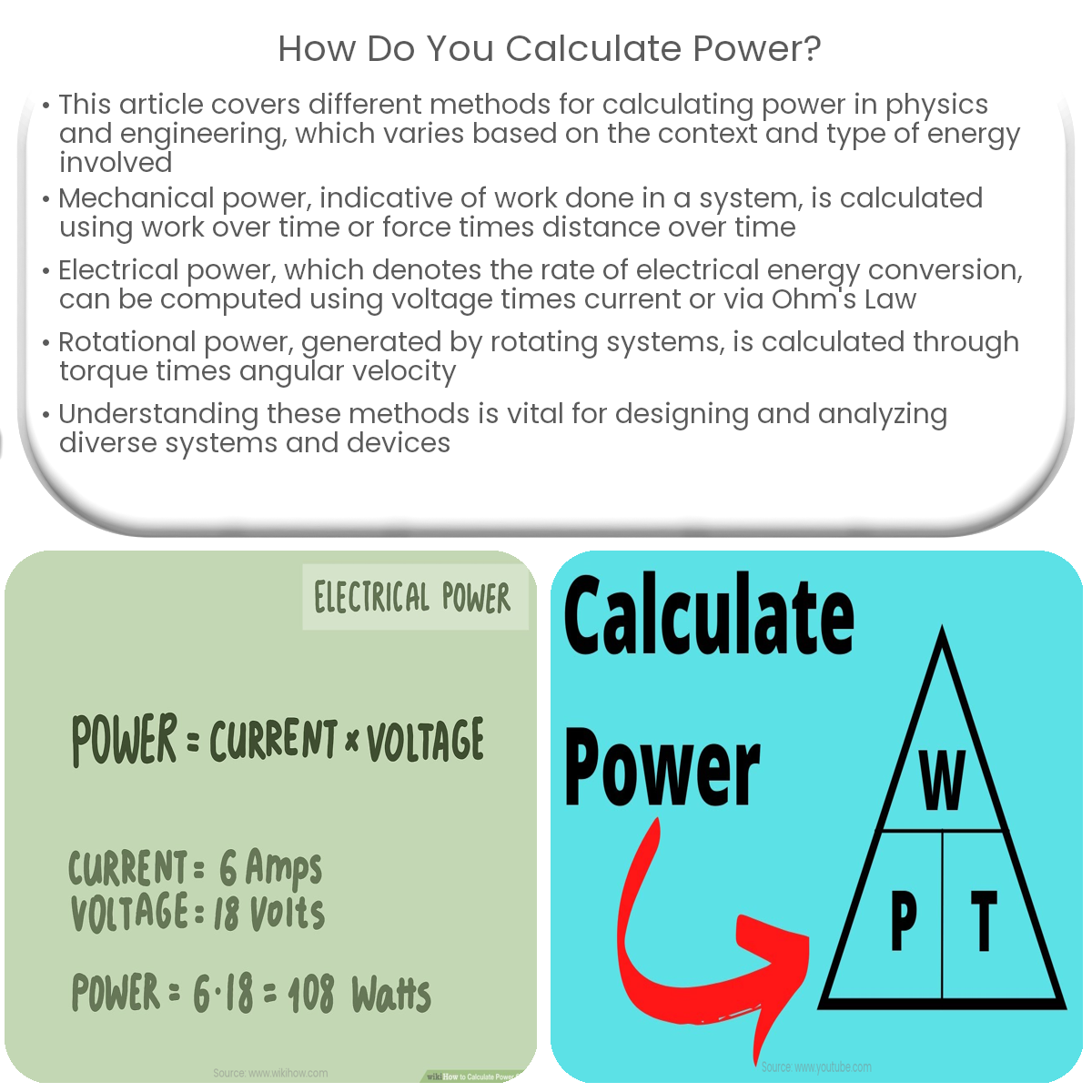
Electrical power is the rate at which electrical energy is converted into other forms of energy, such as heat or mechanical work. It can be calculated using the following formula:
P = V × I
- V: Voltage (measured in volts, V)
- I: Current (measured in amperes, A)
For resistive circuits, electrical power can also be calculated using Ohm’s Law:
P = V2 / R = I2 × R
- R: Resistance (measured in ohms, Ω)
3. Rotational Power
Rotational power is the power generated or consumed by a rotating mechanical system, such as a motor or a generator. It can be calculated using the following formula:
P = τ × ω
- τ: Torque (measured in newton-meters, Nm)
- ω: Angular velocity (measured in radians per second, rad/s)
In conclusion, the calculation of power depends on the type of energy involved and the specific context of the system. Mechanical, electrical, and rotational power can be calculated using different formulas based on the parameters, such as force, distance, time, voltage, current, resistance, torque, and angular velocity. Understanding these methods is crucial for analyzing and designing a wide range of systems and devices.