To calculate impedance in an RLC circuit, find resistance (R), inductive reactance (Xₗ), capacitive reactance (Xc), net reactance (X), and use Z = √(R² + X²).
Calculating Impedance in an RLC Circuit
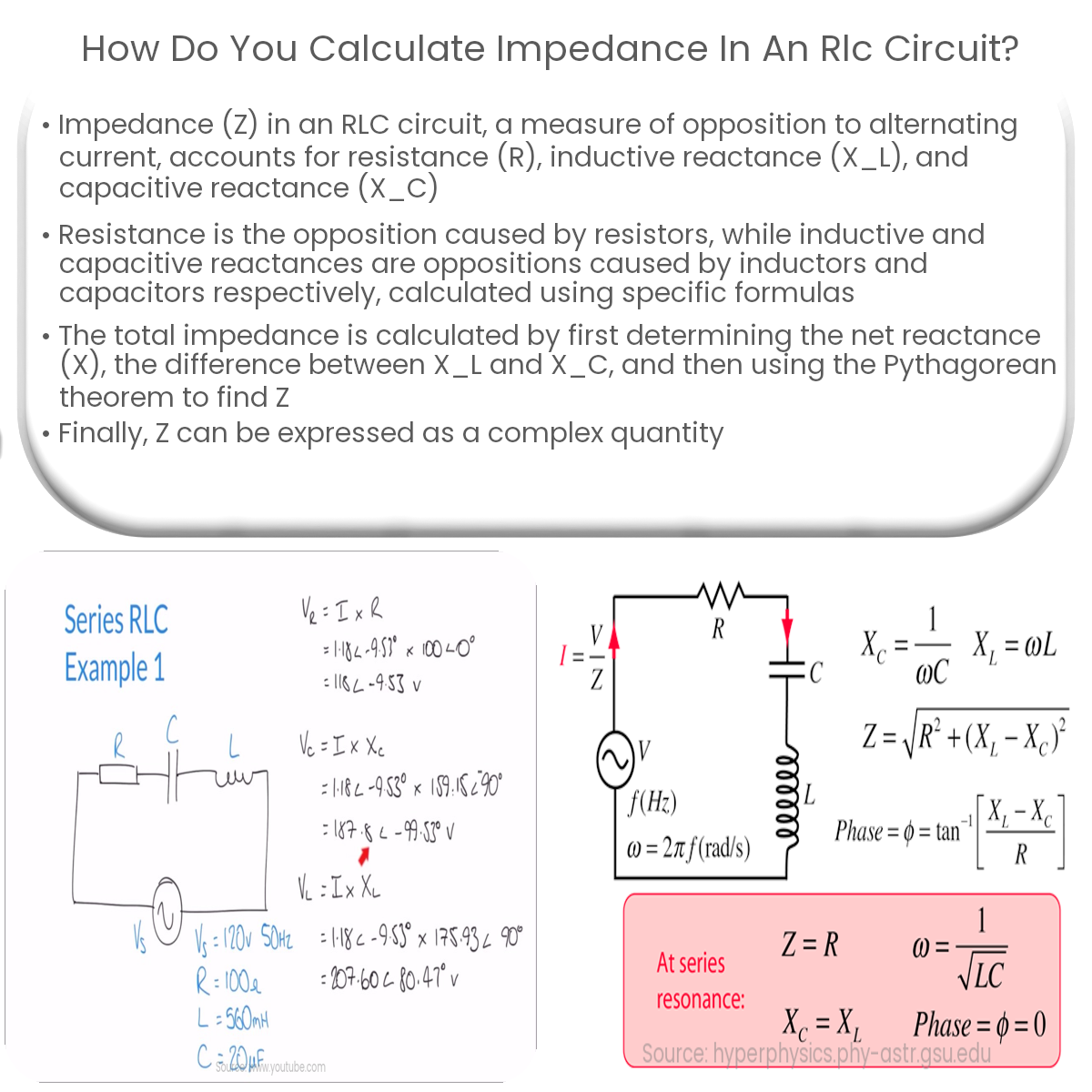
In an RLC circuit, the impedance (Z) is a complex quantity that measures the opposition to the flow of alternating current (AC). It takes into account the resistance (R), inductive reactance (XL), and capacitive reactance (XC) present in the circuit. To calculate the impedance in an RLC circuit, we must first find the values of these individual components.
Finding Resistance, Inductive Reactance, and Capacitive Reactance
The resistance (R) in an RLC circuit is the opposition to the current flow caused by resistors and is measured in ohms (Ω). Inductive reactance (XL) is the opposition to the current flow caused by inductors and is given by the formula:
XL = 2πfL
where f is the frequency of the AC source in hertz (Hz), and L is the inductance of the inductor in henrys (H).
Capacitive reactance (XC) is the opposition to the current flow caused by capacitors and is given by the formula:
XC = 1/(2πfC)
where C is the capacitance of the capacitor in farads (F).
Calculating Total Impedance
Once the values of R, XL, and XC are known, we can calculate the total impedance of the RLC circuit. To do this, we first need to find the net reactance (X), which is the difference between inductive reactance and capacitive reactance:
X = XL – XC
Then, we can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the magnitude of the total impedance (Z):
Z = √(R² + X²)
Finally, to express the impedance as a complex quantity, we can write it in the form Z = R + jX, where j is the imaginary unit.
Summary
Calculating impedance in an RLC circuit involves finding the values of resistance, inductive reactance, and capacitive reactance. The net reactance is obtained by subtracting capacitive reactance from inductive reactance. The magnitude of the total impedance is then calculated using the Pythagorean theorem, and the impedance can be expressed as a complex quantity.