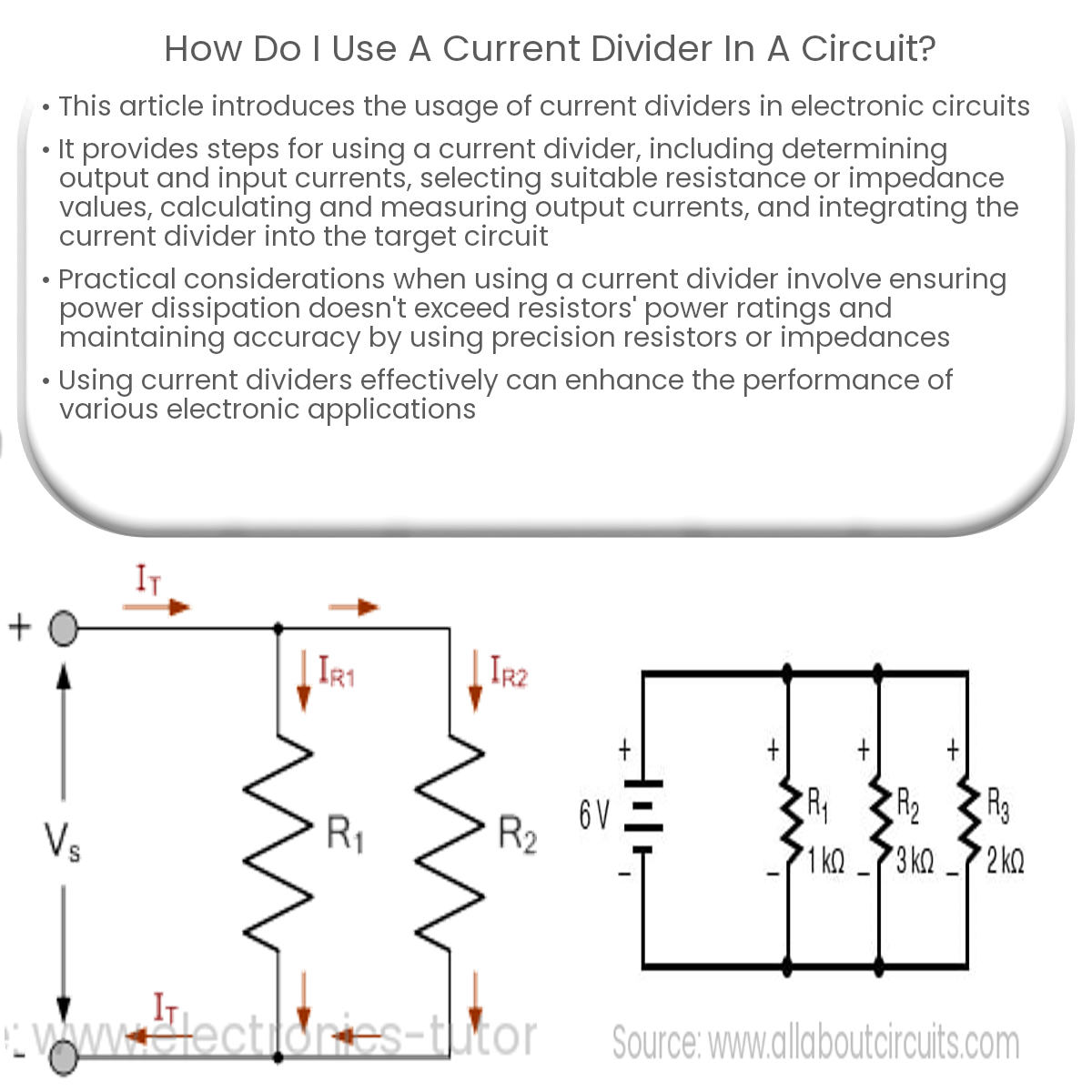
To use a current divider, select resistor values, connect them in parallel, apply input current, measure output currents, and integrate into your circuit.
Introduction to Using Current Dividers
Current dividers are essential components in various electronic circuits for distributing input current among multiple branches. This article will guide you through the process of using a current divider in a circuit.
Steps to Use a Current Divider
- Determine the desired output currents: Before designing the current divider, identify the required output currents (Iout1, Iout2, …) for your specific application.
- Identify the input current: Determine the input current (Iin) that will be applied to the current divider circuit.
- Select appropriate resistor or impedance values: Choose suitable resistance or impedance values (R1, R2, …) for the current divider circuit. The ratio of resistances or impedances determines the distribution of current among the branches.
- Calculate the output currents: Use the current divider formula to verify the output currents: Iout1 = Iin × (R2 / (R1 + R2)).
- Assemble the current divider: Connect the resistors or impedances in parallel, ensuring that the input current is applied to the parallel combination.
- Measure the output currents: Use a multimeter or other current measurement device to confirm the output currents through each resistor or impedance.
- Connect the current divider to the target circuit: Integrate the current divider into your circuit, ensuring that the output currents are connected to the appropriate components or inputs.
Practical Considerations
When using a current divider, it’s important to consider the following aspects:
- Power dissipation: Ensure that the power dissipated by the resistors or impedances in the current divider does not exceed their power rating. Power dissipation can be calculated using the formula P = I² × R, where I is the current flowing through the resistor or impedance.
- Accuracy: Be aware of the tolerance of the resistors or impedances used in the current divider, as this can affect the accuracy of the output currents. Using precision resistors or impedances can improve the accuracy of the current divider.
Conclusion
Using a current divider in a circuit is a straightforward process that involves selecting appropriate resistor or impedance values, assembling the current divider, and integrating it into your target circuit. By considering power dissipation and accuracy, you can effectively use current dividers in various electronic applications.