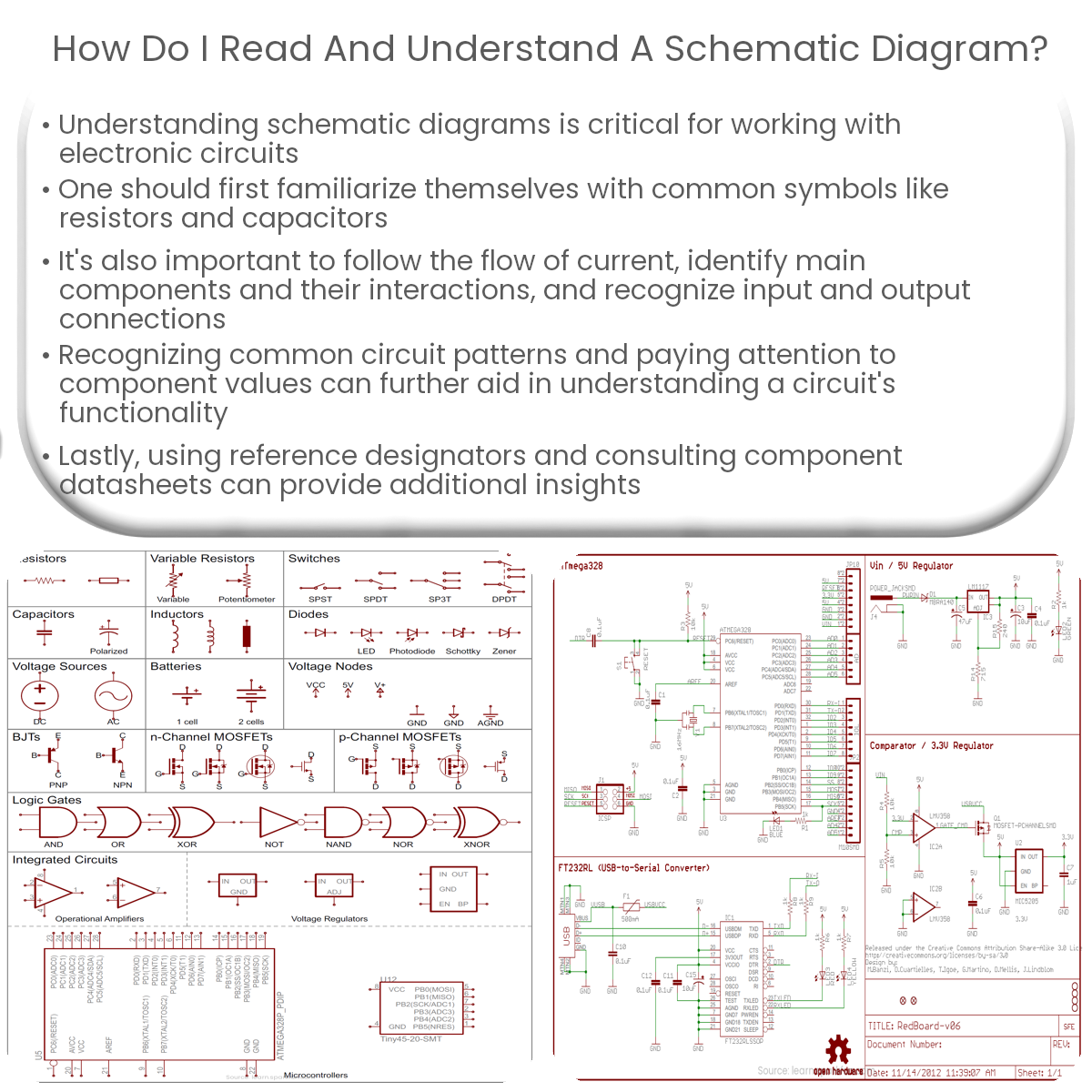
To read a schematic, learn common symbols, follow current flow, identify main components, study input/output connections, recognize patterns, and consult datasheets.
Reading and Understanding a Schematic Diagram
A schematic diagram is an essential tool for understanding electronic circuits. It uses standardized symbols to represent components and their connections. Here’s a guide on how to read and understand a schematic diagram.
1. Familiarize yourself with common symbols
Start by learning the most common symbols used in schematics, such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, and transistors. Recognizing these symbols will help you decipher the circuit’s layout and function.
2. Follow the flow of current
Electrical current typically flows from the positive (+) terminal to the negative (-) terminal. In a schematic, follow the current flow by tracing the lines connecting components. This will give you an idea of how the circuit operates.
3. Identify the main components and subsystems
Examine the schematic for key components, such as power supplies, microcontrollers, and sensors. Understand the role of each component and how they interact within the circuit. Group related components into subsystems to simplify your analysis.
4. Study the input and output connections
Identify the input and output connections on the schematic. Inputs can include power sources, sensors, or switches, while outputs can consist of motors, lights, or speakers. Recognizing these connections will help you understand the purpose of the circuit.
5. Look for common circuit patterns
Many circuits share similar building blocks, such as amplifiers, filters, or voltage regulators. Familiarize yourself with these common patterns to quickly understand the circuit’s functionality.
6. Pay attention to component values
Component values, such as resistance or capacitance, are often indicated on the schematic. These values are essential in determining the circuit’s behavior and performance.
7. Use the reference designators
Reference designators, such as R1 for a resistor or C1 for a capacitor, help you locate components on the schematic and the physical circuit board. They can also assist in troubleshooting and assembly.
8. Consult the datasheets
When working with unfamiliar components, consult their datasheets for specifications and application information. Datasheets can provide valuable insight into how the component functions within the circuit.
Conclusion
Reading and understanding schematic diagrams takes practice, but it’s an essential skill for anyone working with electronics. By familiarizing yourself with common symbols, analyzing the current flow, and identifying key components, you’ll be well on your way to deciphering complex circuits.