Electrostatic loudspeakers work by using electrostatic forces to control a thin diaphragm’s movement, producing high-quality sound reproduction.
How Do Electrostatic Loudspeakers Work?
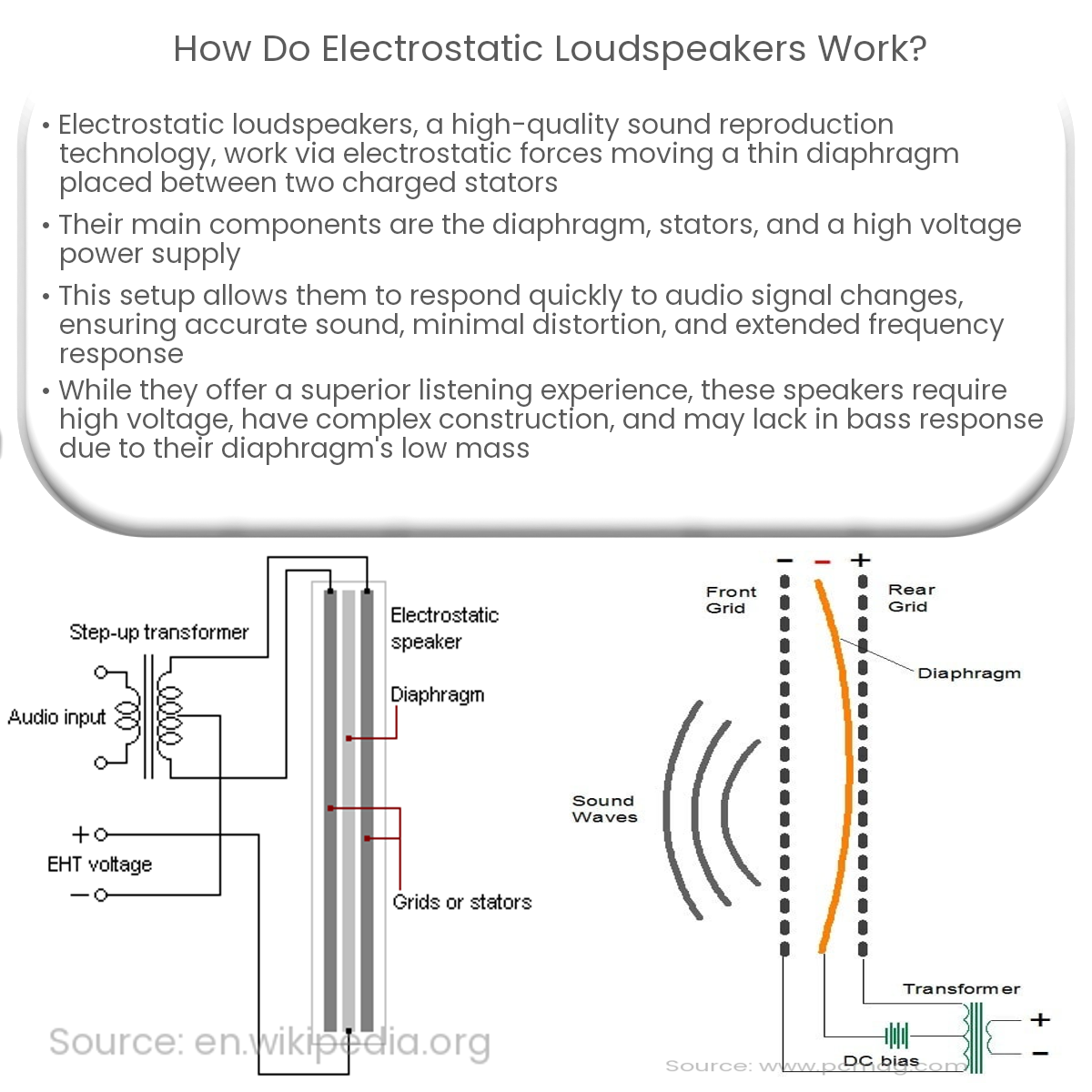
Electrostatic loudspeakers are a unique and advanced type of speaker technology that offers high-quality sound reproduction. They operate using the principle of electrostatic forces to move a thin diaphragm placed between two charged stators. This article will explore the working mechanism of electrostatic loudspeakers and their key components.
Components of Electrostatic Loudspeakers
An electrostatic loudspeaker consists of three primary components:
- Diaphragm: A thin, lightweight, and electrically conductive film that vibrates to produce sound.
- Stators: Two perforated metal plates placed on either side of the diaphragm, holding a constant high voltage charge.
- Power supply: Provides the high voltage needed to create an electrostatic field between the stators and diaphragm.
Working Principle of Electrostatic Loudspeakers
The operation of an electrostatic loudspeaker can be broken down into a series of steps:
- The power supply generates a high voltage, which charges the stators with an electrostatic field.
- The diaphragm is also given a charge, which creates an electrostatic force between it and the stators.
- When an audio signal is applied to the stators, the electrostatic field between them and the diaphragm varies.
- The varying electrostatic forces cause the diaphragm to move, creating vibrations that produce sound waves.
Due to the lightweight nature of the diaphragm and the absence of a conventional voice coil and magnet, electrostatic loudspeakers can respond quickly to changes in the audio signal. This results in highly accurate sound reproduction, minimal distortion, and an extended frequency response.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Electrostatic loudspeakers offer several advantages over traditional dynamic speakers:
- Higher fidelity sound reproduction due to the lightweight diaphragm and precise control of electrostatic forces.
- Minimal distortion and an extended frequency response.
- Wide dispersion of sound, leading to a larger “sweet spot” for listeners.
However, there are also some drawbacks:
- High voltage requirements and complex construction, making them more expensive and less common than dynamic speakers.
- Large size and limited bass response due to the diaphragm’s low mass and the need for a large surface area to produce adequate sound levels.
In conclusion, electrostatic loudspeakers work by using electrostatic forces to control the movement of a thin diaphragm, resulting in high-quality sound reproduction. While they have some disadvantages, they remain a popular choice for audiophiles seeking an accurate and immersive listening experience.