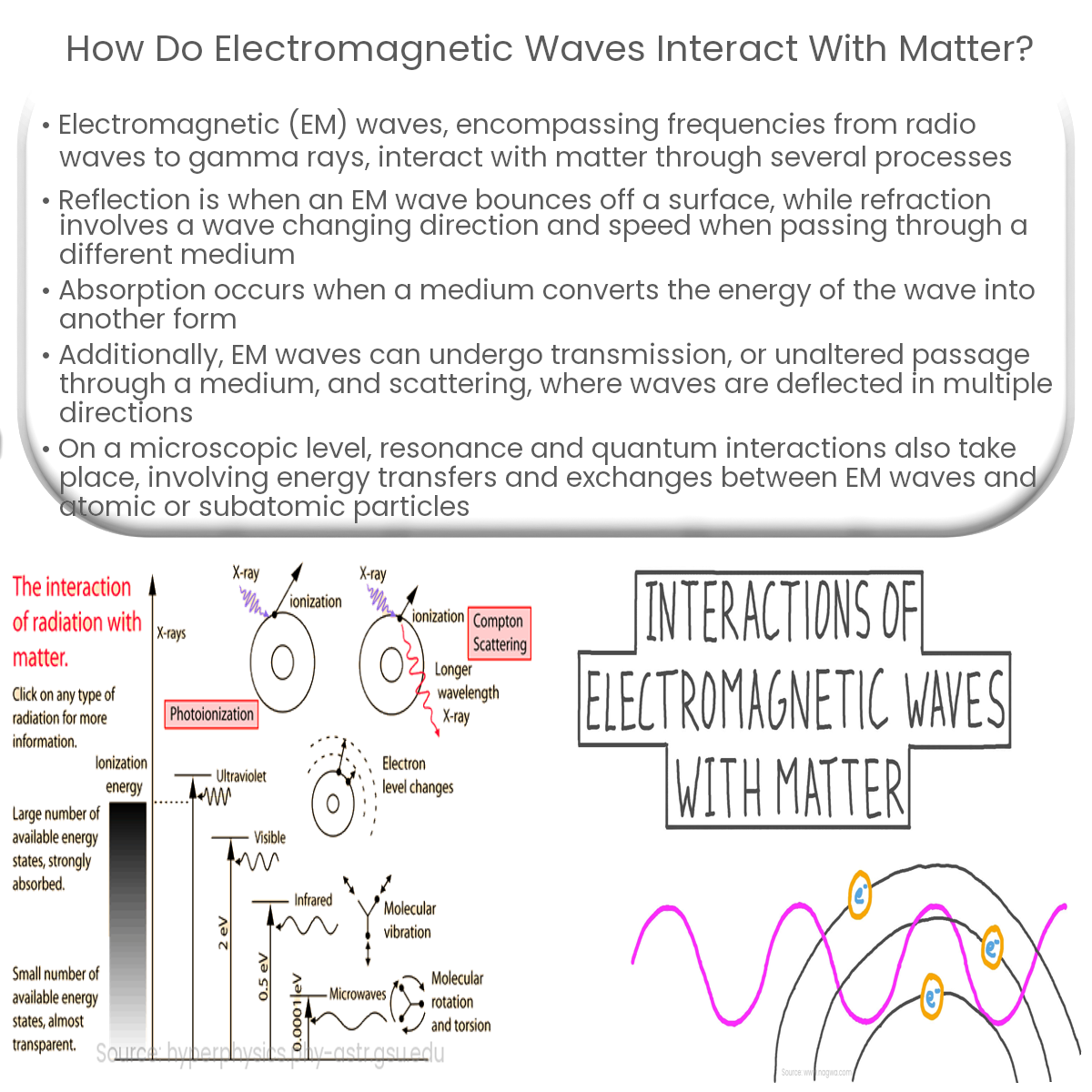
Electromagnetic waves interact with matter through reflection, refraction, absorption, transmission, scattering, resonance, and quantum interactions.
How Do Electromagnetic Waves Interact with Matter?
Electromagnetic (EM) waves encompass a broad spectrum of frequencies, from radio waves to gamma rays. They play a vital role in our daily lives, powering technologies like cell phones and microwaves. But how do these waves interact with matter? This article delves into the mechanisms that govern these interactions.
Reflection, Refraction, and Absorption
When an EM wave encounters matter, it can undergo reflection, refraction, or absorption. These processes are dependent on the properties of the medium and the frequency of the wave.
Reflection occurs when a wave bounces off a surface, changing its direction but maintaining its frequency. Smooth surfaces, like mirrors, reflect light in a predictable manner.
Refraction happens when a wave changes direction and speed as it passes through a medium with a different refractive index. This phenomenon is responsible for the bending of light through lenses and water.
Absorption takes place when a medium converts the energy of an EM wave into another form, such as heat or vibration. This process attenuates the wave, reducing its amplitude and intensity.
Transmission and Scattering
In addition to the above processes, EM waves can also undergo transmission and scattering when interacting with matter.
Transmission is the passage of EM waves through a medium without significant alteration. An example of this is light passing through a clear glass window.
Scattering occurs when EM waves are deflected in multiple directions by particles or irregularities in a medium. Scattering is responsible for phenomena like the blue sky and the reddening of the sun during sunset.
Resonance and Quantum Interactions
At a microscopic level, EM waves can interact with matter through resonance and quantum interactions.
Resonance is the transfer of energy between an EM wave and an oscillating system, such as an electron in an atom. This transfer can lead to absorption or emission of photons, which are the particles that make up EM waves.
Quantum interactions involve the discrete exchange of energy between EM waves and subatomic particles. The photoelectric effect, in which photons knock electrons out of a material, exemplifies this interaction.
In summary, the interaction of electromagnetic waves with matter can involve reflection, refraction, absorption, transmission, scattering, resonance, and quantum interactions. These processes are crucial for understanding the behavior of light and other EM waves in various contexts, from communication technologies to natural phenomena.