Diodes work by allowing current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite, utilizing the properties of P-type and N-type materials.
Understanding Diodes
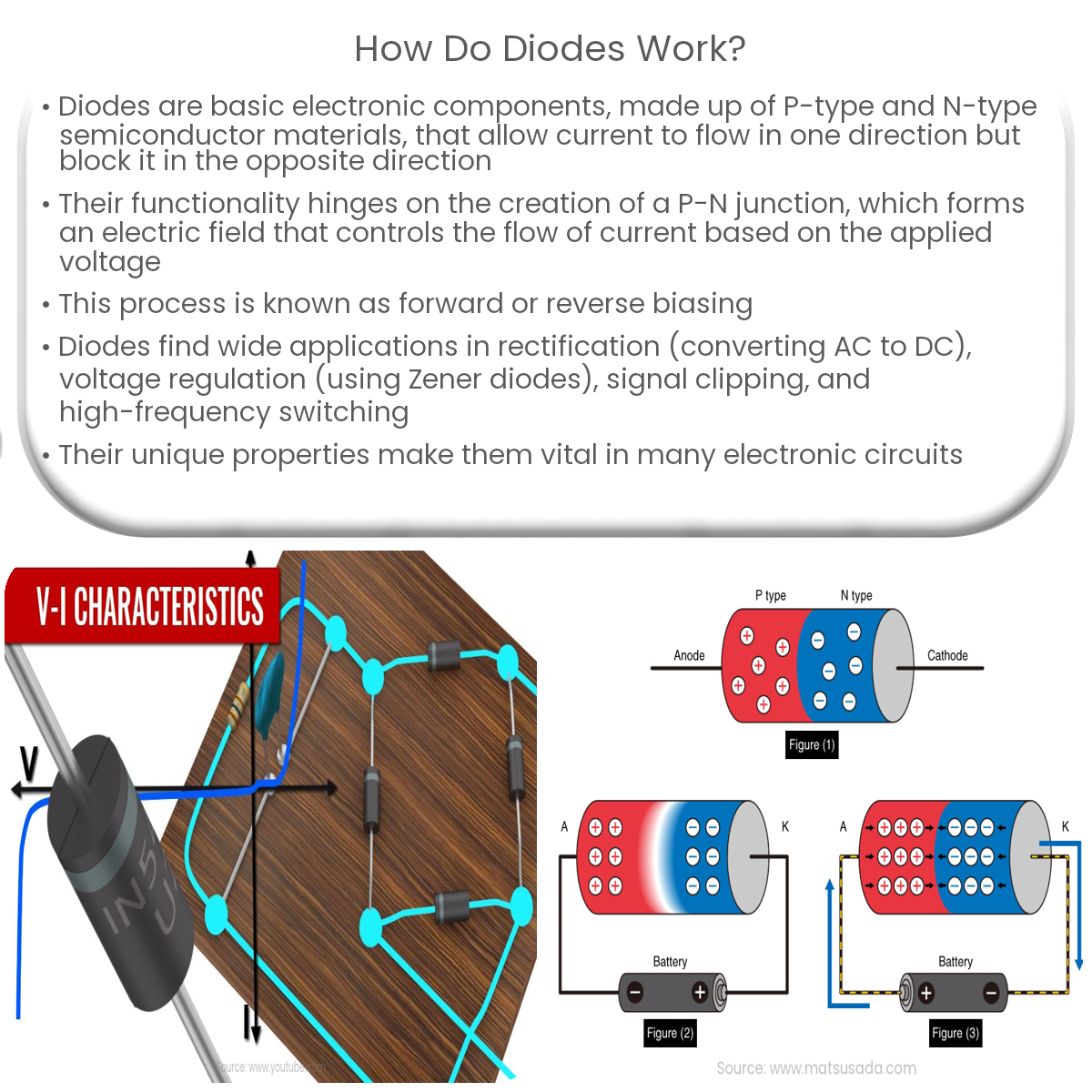
A diode is a fundamental electronic component that allows current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. It consists of two layers of semiconductor material, known as the P-type and the N-type, which are joined together to create a junction called the P-N junction.
How Diodes Work
Diodes work by taking advantage of the unique properties of P-type and N-type semiconductor materials. P-type material contains an excess of positive charge carriers called holes, while N-type material has an excess of negative charge carriers called electrons. When the P-type and N-type materials are joined to create a P-N junction, some electrons from the N-type side migrate to the P-type side and recombine with holes, creating a region known as the depletion layer. This migration results in an electric field, which prevents further flow of charge carriers across the junction.
When a voltage is applied across the diode in the forward direction (positive voltage to the P-type side and negative voltage to the N-type side), the electric field at the junction is reduced, allowing the flow of current. This is called forward biasing. On the other hand, when a reverse voltage is applied (negative voltage to the P-type side and positive voltage to the N-type side), the electric field at the junction is increased, preventing the flow of current. This is called reverse biasing.
Applications of Diodes
- Rectification: Diodes are widely used in rectifier circuits, which convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). This is achieved by allowing the flow of current in one direction only.
- Voltage Regulation: Zener diodes are a special type of diode that can maintain a constant voltage across its terminals under reverse bias, making them ideal for voltage regulation applications.
- Signal Clipping and Limiting: Diodes can be used to limit or clip a signal’s voltage to a specific level, which can be useful in various signal processing applications.
- Switching: Fast switching diodes are used in high-frequency applications where rapid on-off transitions are required.
In summary, diodes are essential electronic components that work by allowing current flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. Their unique properties make them indispensable in a variety of applications, including rectification, voltage regulation, signal clipping, and high-frequency switching.