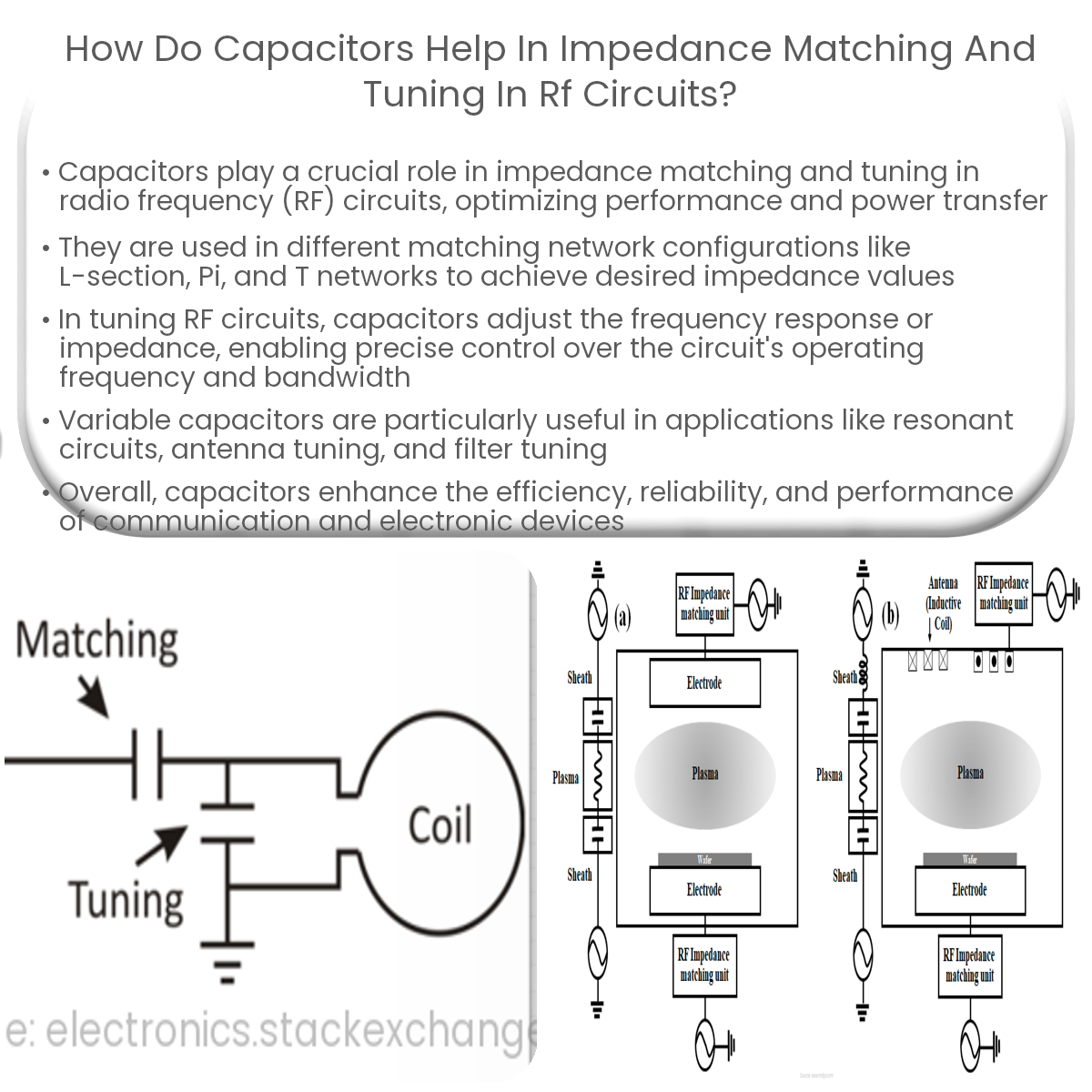
Capacitors help in impedance matching and tuning in RF circuits by forming matching networks, adjusting resonant frequency, and fine-tuning frequency response.
Capacitors in Impedance Matching and Tuning in RF Circuits
Impedance matching and tuning are critical aspects of radio frequency (RF) circuit design. Capacitors play a significant role in achieving these objectives, ensuring optimal performance and power transfer in RF systems. This article discusses how capacitors contribute to impedance matching and tuning in RF circuits.
Impedance Matching
In RF circuits, impedance matching is essential to minimize signal reflections and maximize power transfer between different stages or components. Mismatches in impedance can lead to signal loss, distortion, and reduced system efficiency. Capacitors are commonly used in combination with inductors or other capacitors to form impedance matching networks.
There are various matching network configurations, including L-section, Pi, and T networks, which employ capacitors to achieve the desired impedance values:
Tuning in RF Circuits
Tuning is the process of adjusting the frequency response of an RF circuit, such as an amplifier, filter, or oscillator, to achieve the desired operating frequency and bandwidth. Capacitors are used in tuning networks to adjust the resonant frequency or impedance of the circuit.
Variable capacitors, also known as trimmer capacitors or tuning capacitors, are often used for tuning purposes. They allow for precise adjustments to the capacitance value, enabling the fine-tuning of the circuit’s frequency response or impedance. Common tuning applications involving capacitors include:
In conclusion, capacitors are essential components in impedance matching and tuning of RF circuits. They contribute to the efficient power transfer and precise frequency control in RF systems, enhancing the overall performance and reliability of communication and electronic devices.