Capacitive pressure sensors detect pressure changes by measuring capacitance variations between two conductive plates.
Introduction
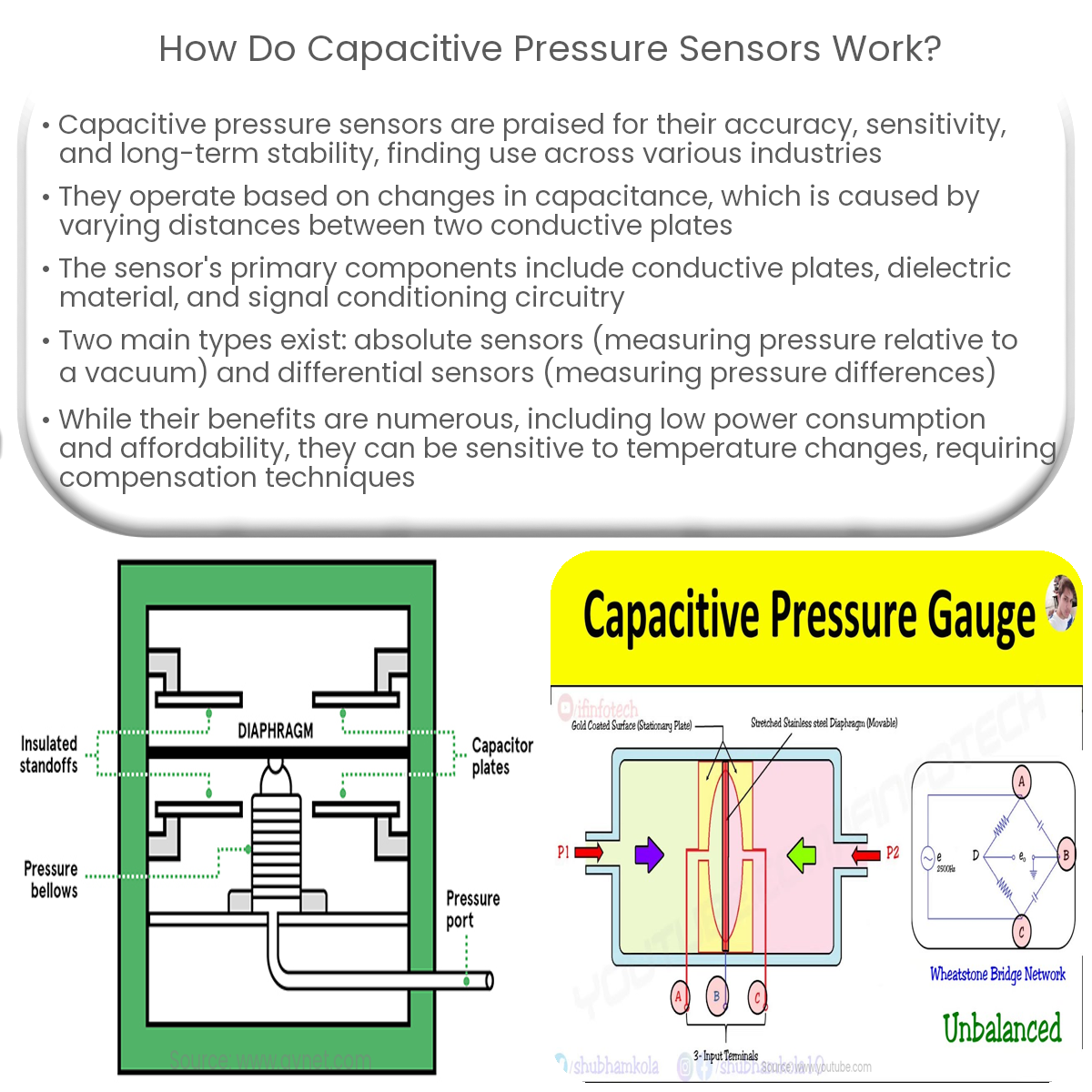
Capacitive pressure sensors are widely used in various industries for their accuracy, sensitivity, and long-term stability. They work by detecting changes in capacitance resulting from variations in the distance between two conductive plates. This article will discuss the working principle of capacitive pressure sensors and the key components involved.
Working Principle
A capacitive pressure sensor consists of two parallel conductive plates separated by a dielectric material. When pressure is applied to the sensor, it causes a deformation in one or both of the conductive plates, altering the distance between them. This change in distance, in turn, affects the capacitance between the plates. By measuring the change in capacitance, the applied pressure can be determined.
Key Components
- Conductive Plates: These are typically made of metal or other conductive materials and form the primary sensing element of the sensor. The plates are placed parallel to each other, with one fixed and the other movable, allowing for changes in distance due to pressure variations.
- Dielectric Material: Positioned between the conductive plates, the dielectric material serves to insulate the plates from each other and store electrical energy. Common dielectric materials used in capacitive pressure sensors include air, glass, ceramics, and polymers.
- Signal Conditioning Circuitry: This component converts the capacitance changes into an electrical signal that can be easily measured and analyzed. The signal conditioning circuitry usually includes a capacitance-to-voltage converter, amplifier, and sometimes a microcontroller for additional processing.
Types of Capacitive Pressure Sensors
There are two main types of capacitive pressure sensors: absolute and differential. Absolute capacitive pressure sensors measure pressure relative to a vacuum, while differential capacitive pressure sensors measure the difference in pressure between two points. The choice of sensor type depends on the specific application requirements.
Advantages and Limitations
Capacitive pressure sensors offer several advantages over other types of pressure sensors, such as their high sensitivity, accuracy, and low power consumption. Additionally, they can be made with relatively simple and low-cost manufacturing processes. However, capacitive pressure sensors can be susceptible to temperature variations, which can affect their performance. To mitigate this issue, temperature compensation techniques are often employed.
Conclusion
Capacitive pressure sensors play a crucial role in numerous applications, from industrial process control to medical devices. By understanding how they work and their key components, engineers can select the right sensor for their specific application and optimize the performance of the overall system.