Batteries work in circuits by providing voltage, storing and releasing energy, and powering devices when connected in series or parallel configurations.
Introduction to Batteries in Circuits
Batteries play a crucial role in powering various electronic devices and systems. Understanding how batteries work in a circuit can help you design and maintain more efficient and reliable systems. This article will discuss the role and function of batteries in electronic circuits.
Components of a Battery
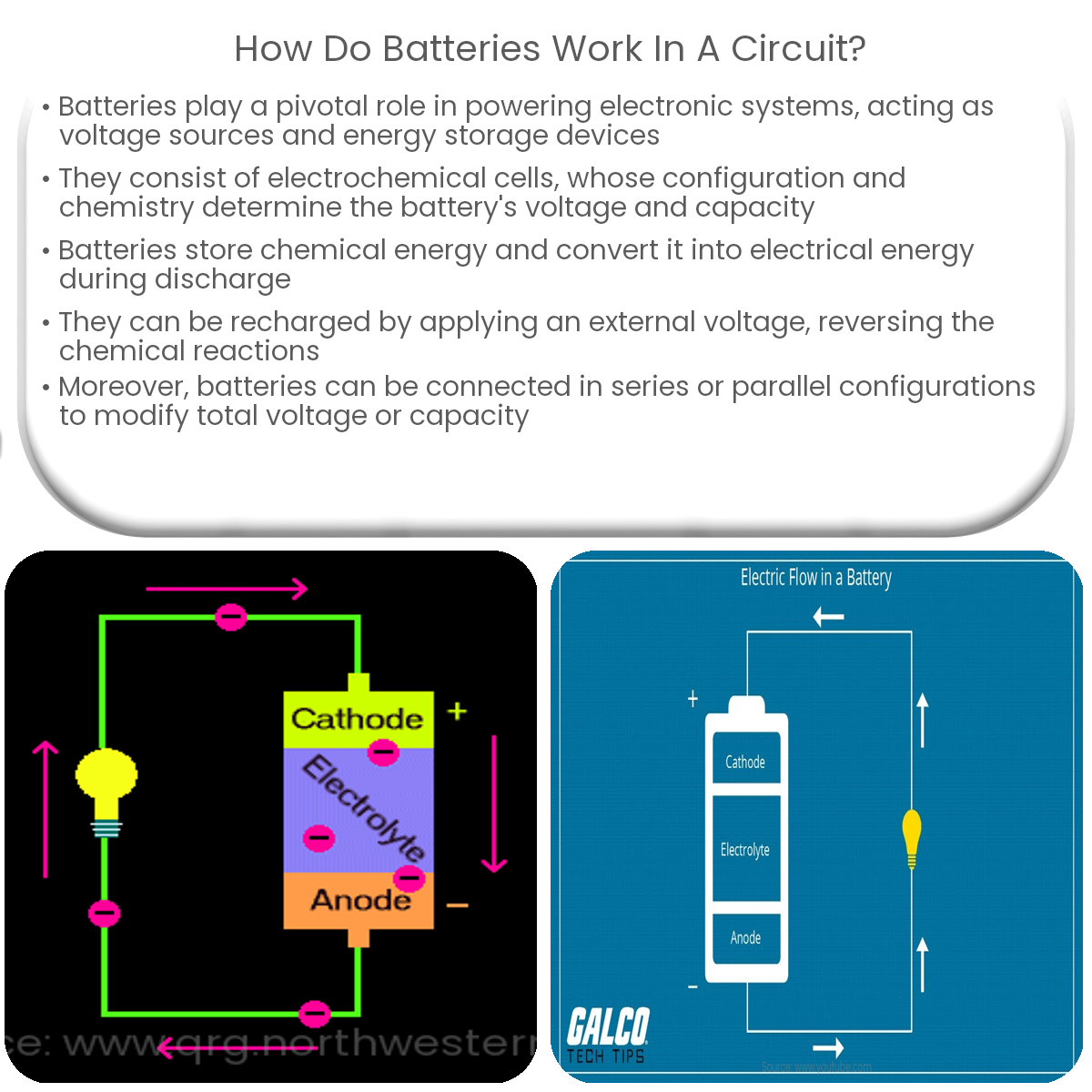
A battery consists of electrochemical cells that generate electric current through chemical reactions. Each cell has a positive and a negative electrode, and an electrolyte that facilitates the chemical reaction. The battery’s voltage and capacity depend on the cell’s electrochemistry and configuration.
Batteries as Voltage Sources
In a circuit, a battery acts as a voltage source, providing a potential difference between its positive and negative terminals. This potential difference, or voltage, drives the flow of electric current through the circuit. The direction of the current depends on the battery’s polarity, with the current flowing from the positive terminal to the negative terminal.
Energy Storage and Release
Batteries store energy in the form of chemical energy, which is converted into electrical energy during discharge. The amount of energy a battery can store is determined by its capacity, measured in ampere-hours (Ah) or milliampere-hours (mAh). The capacity indicates the amount of current a battery can provide for a specific duration. During discharge, the battery’s chemical energy is released as electrical energy, powering the connected devices in the circuit.
Battery Charging
Rechargeable batteries can be charged by applying an external voltage source to the battery terminals, reversing the chemical reactions that occur during discharge. This process restores the battery’s chemical energy, allowing it to be used again. It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for charging rates and voltages to ensure battery longevity and safety.
Series and Parallel Battery Configurations
Batteries can be connected in series or parallel configurations to achieve different voltage and capacity levels in a circuit:
- Series connection: Connecting batteries in series increases the total voltage while keeping the capacity constant. For example, two 1.5V AA batteries connected in series will provide a combined voltage of 3V.
- Parallel connection: Connecting batteries in parallel increases the total capacity while keeping the voltage constant. For example, two 1.5V AA batteries connected in parallel will provide a combined capacity of twice the capacity of a single battery.
Conclusion
Batteries are essential components in electronic circuits, acting as voltage sources, energy storage devices, and power providers. Understanding how batteries function in a circuit and the different ways they can be connected can help you design more efficient and reliable systems.