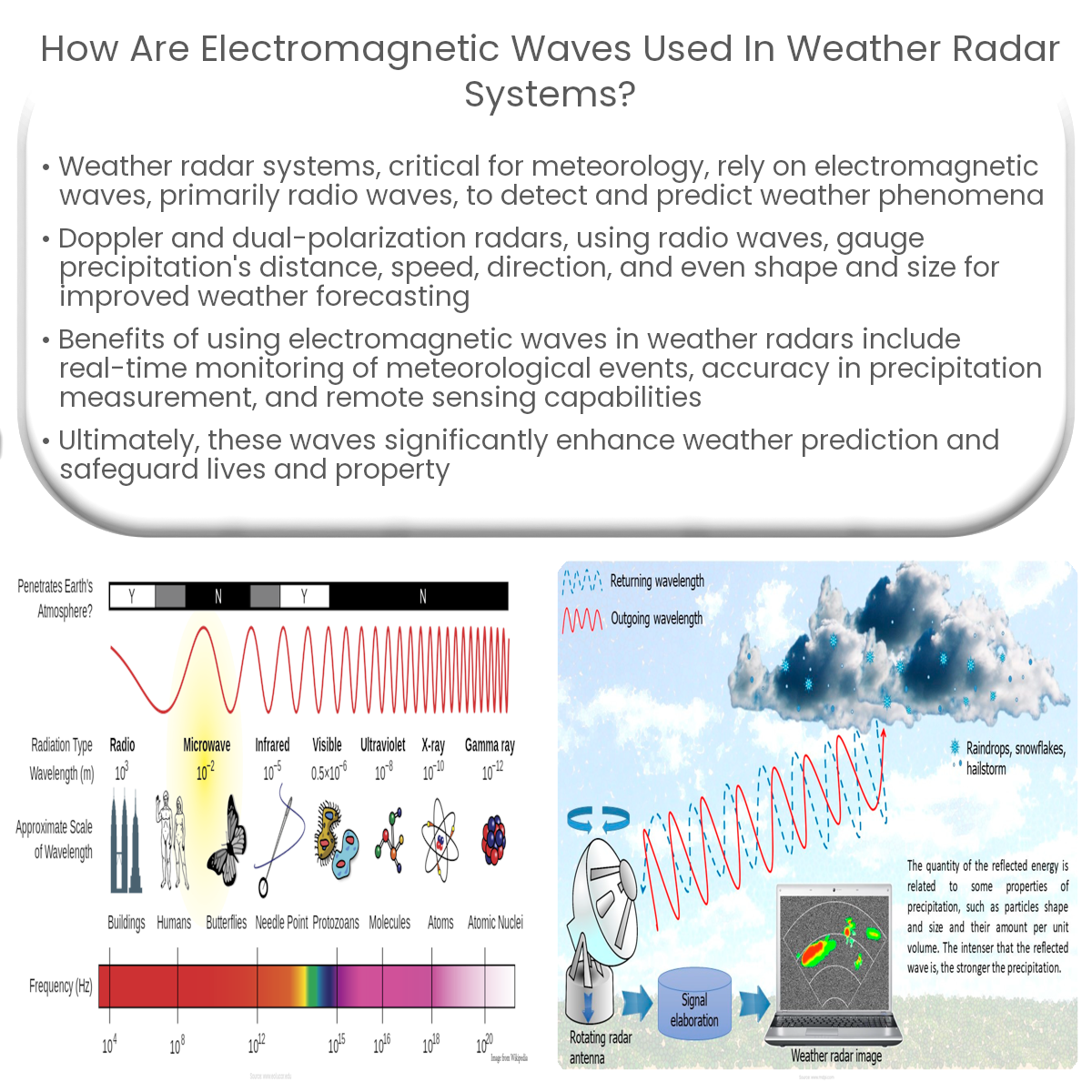
Electromagnetic waves, specifically radio waves, are used in weather radar systems to detect precipitation and monitor meteorological phenomena.
Electromagnetic Waves in Weather Radar Systems
Weather radar systems play a crucial role in meteorology, providing accurate and timely data to monitor and predict weather patterns. These systems rely on electromagnetic waves, specifically radio waves, to detect precipitation and other meteorological phenomena. This article delves into how electromagnetic waves are utilized in weather radar systems for effective weather forecasting.
Understanding Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves are a type of energy that travel through space or other medium, composed of electric and magnetic fields oscillating perpendicular to each other. They cover a broad spectrum, ranging from radio waves to gamma rays, with varying frequencies and wavelengths. Weather radar systems primarily use radio waves, which have longer wavelengths and lower frequencies compared to other types of electromagnetic waves.
How Weather Radar Systems Work
- Doppler radar: The most common type of weather radar, Doppler radar, sends out radio waves in pulses and measures the time taken for these waves to bounce back after hitting precipitation particles, such as raindrops or snowflakes. The time delay helps determine the distance of the precipitation from the radar, while the frequency shift of the reflected waves provides information on the speed and direction of the precipitation.
- Dual-polarization radar: An advanced version of the Doppler radar, dual-polarization radar, emits radio waves in both horizontal and vertical orientations. By analyzing the differences in the return signals from these two orientations, meteorologists can gain a better understanding of the shape and size of precipitation particles, improving the accuracy of precipitation type classification and rainfall estimation.
Benefits of Using Electromagnetic Waves in Weather Radar
- Real-time monitoring: Electromagnetic waves enable weather radar systems to provide real-time data on precipitation, wind, and even tornadoes, allowing for prompt warnings and ensuring public safety.
- Accuracy: The use of radio waves in weather radar systems facilitates accurate measurement of precipitation location, intensity, and movement, resulting in more precise weather forecasting.
- Remote sensing: Since radio waves can travel long distances without being absorbed or scattered by the atmosphere, weather radar systems can effectively detect meteorological phenomena in remote areas, even in challenging weather conditions.
In conclusion, electromagnetic waves, particularly radio waves, are an essential component of weather radar systems. They enable accurate and real-time monitoring of precipitation and other meteorological phenomena, improving weather forecasting and ultimately safeguarding lives and property.