Explore the role of fixed voltage regulators in maintaining stable voltage in electronic systems, their types, applications, advantages, and limitations.
Introduction to Fixed Voltage Regulators
A fixed voltage regulator is a critical electronic component that maintains a constant output voltage level regardless of changes in the input voltage or load conditions. It is an essential device used in a variety of applications, from computers and communication devices to home appliances and automobiles.
Understanding the Concept of Voltage Regulation
Voltage regulation refers to the process of maintaining a constant level of voltage in an electrical circuit. In an ideal situation, the output voltage of a power supply should remain steady, even if the input voltage or the load resistance changes. However, in the real world, voltage variations are commonplace due to fluctuations in the power grid, varying load demands, and other factors. This is where voltage regulators come in.
The Role of Fixed Voltage Regulators
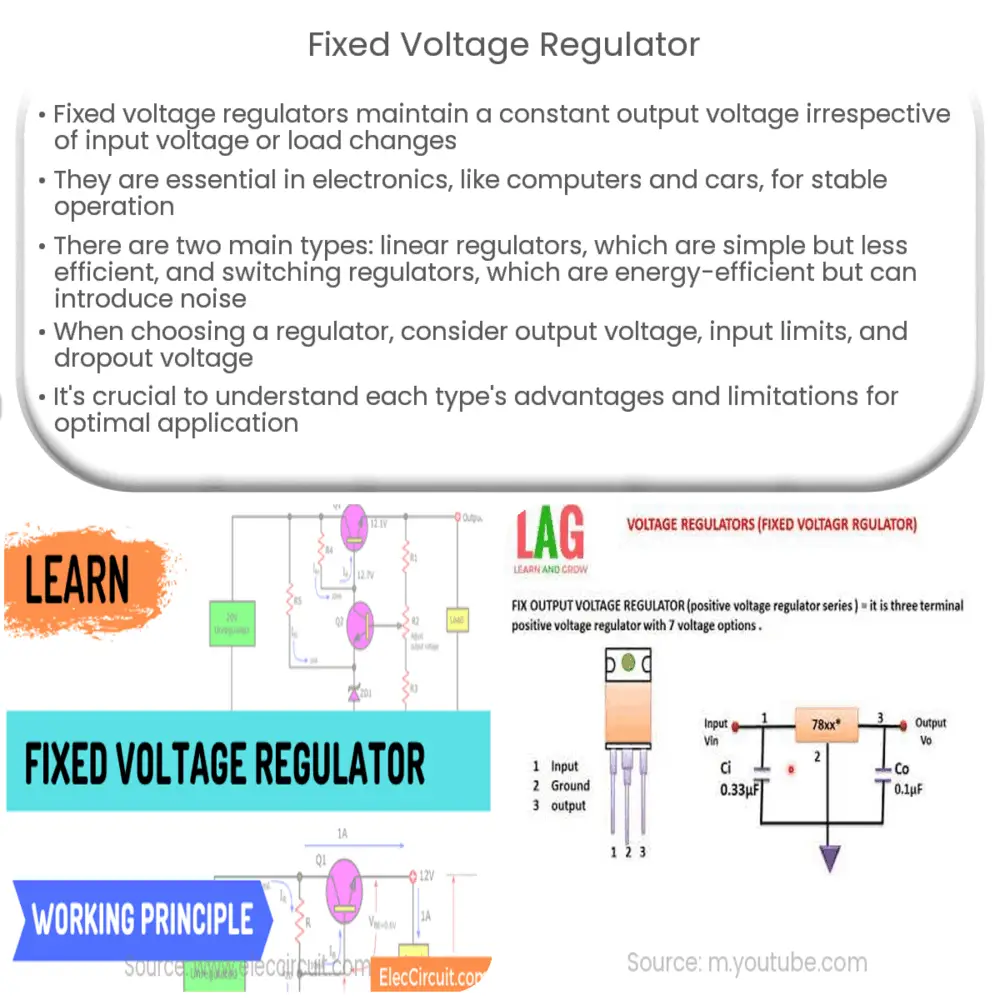
A fixed voltage regulator, as the name suggests, provides a fixed output voltage. It means that no matter what variations occur in the input voltage or load, the output voltage remains the same. There are different types of fixed voltage regulators, including linear regulators and switching regulators, each with their unique characteristics and applications.
- Linear Regulators: A linear regulator works by dissipating excess voltage in the form of heat to maintain a constant output voltage. They are simple, cost-effective, and provide clean, noise-free output voltage. However, their efficiency is not high, especially when there is a large difference between input and output voltage.
- Switching Regulators: Unlike linear regulators, switching regulators work by turning the power switch on and off at a high frequency. This method is more energy-efficient, but it can introduce noise into the output voltage, which may not be suitable for sensitive electronic devices.
Key Specifications of Fixed Voltage Regulators
When selecting a fixed voltage regulator, several important specifications need to be considered. The output voltage is, of course, the primary specification. This value is often indicated in the regulator’s name, such as a 7805 regulator which outputs a fixed voltage of 5V. Other important considerations include the maximum input voltage, maximum output current, and the dropout voltage, which is the minimum difference between input and output voltage needed for the regulator to function properly.
How Fixed Voltage Regulators Work
The working principle of a fixed voltage regulator is straightforward. When the input voltage, or the voltage across the regulator, exceeds the desired output voltage, the regulator reduces the excess voltage. This reduction process varies depending on the type of regulator.
In a linear regulator, the excess voltage is dissipated as heat, hence the need for a heat sink in high-power applications. In contrast, a switching regulator reduces the voltage by quickly switching the internal transistor on and off.
Applications of Fixed Voltage Regulators
Fixed voltage regulators find a wide range of applications. They are used extensively in power supplies for electronic devices such as computers, televisions, and radios, where a constant voltage level is crucial. They are also found in battery chargers, where they help maintain a steady charging voltage, and in automotive electronics, to regulate the voltage provided to different components.
Advantages and Limitations
- Advantages: The key advantage of fixed voltage regulators is their simplicity and reliability. They provide a stable output voltage, irrespective of input voltage fluctuations or variations in load conditions. They are also relatively inexpensive and easy to use, making them a popular choice for a variety of applications.
- Limitations: Despite their benefits, fixed voltage regulators do have limitations. Linear regulators can be inefficient, especially when there is a large voltage difference between input and output. Switching regulators, although more efficient, can generate noise that may interfere with other electronic components.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fixed voltage regulators play a vital role in various electronic systems by providing a constant output voltage. They mitigate the problems caused by voltage fluctuations, ensuring the stable operation of electronic devices. Whether it’s the simplicity and noise-free operation of linear regulators or the energy efficiency of switching regulators, each type offers unique advantages to meet diverse requirements. However, it’s also important to understand their limitations and select the most suitable regulator based on the specific needs of the application. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more efficient and versatile voltage regulators in the future.

