Explore the workings, applications, and future prospects of Dual Speed Induction Motors in our comprehensive guide.
Introduction to Dual Speed Induction Motors
Induction motors have been a cornerstone in the field of electromechanical energy conversion due to their high reliability, robustness, and efficiency. A variant of these induction motors, known as the Dual Speed Induction Motor, has found extensive applications in diverse fields. These motors, as the name suggests, offer two distinct speed levels, providing a high level of versatility and control.
Working Principle of Dual Speed Induction Motors
Before diving into the details of dual speed induction motors, it’s essential to understand the fundamental working principle of a regular induction motor. An induction motor works on the principle of electromagnetic induction where the alternating current passing through the stator winding induces a rotating magnetic field. This magnetic field then induces a current in the rotor winding, causing it to rotate and generate torque.
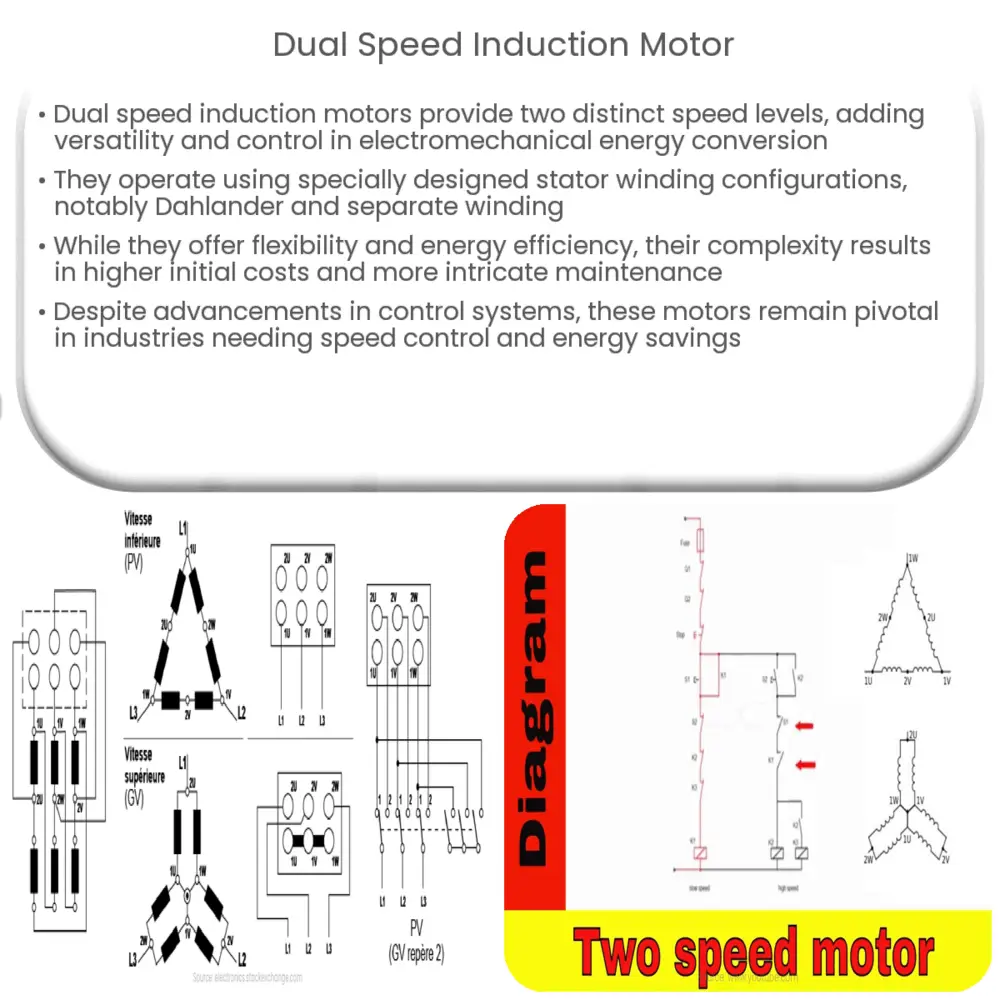
The unique feature of the dual speed induction motor is its ability to run at two distinct speeds. This is achieved through a specially designed stator winding configuration, which can be wired in two different ways, altering the number of magnetic poles, and thereby changing the motor’s speed.
Stator Winding Configurations
The stator winding configuration is the key to the dual speed capability. Two common configurations are the Dahlander winding (also known as a pole-changing winding) and separate winding.
- Dahlander Winding: Named after its inventor, Fritz Dahlander, this configuration has two distinct speed ratios, typically 1:2 or 1:3. Depending on the switching, it can generate either double or triple the number of poles, thereby halving or reducing the speed to a third.
- Separate Winding: This configuration uses two independent windings, each designed for a specific number of poles. The speeds can be switched by energizing the respective winding. This design offers more flexibility in speed ratios compared to Dahlander winding.
These winding configurations provide the versatility required in many applications. For instance, in applications like pumps, fans, or blowers, different speeds may be required based on the load conditions. Dual speed induction motors with their two distinct speed levels cater to these requirements efficiently.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dual Speed Induction Motors
Like any technological solution, dual speed induction motors come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. The primary advantage is the ability to control the speed, thereby offering increased flexibility and efficiency. The user can switch to the desired speed based on the operational requirements, leading to energy savings.
On the downside, the complexity of the motor increases due to the dual winding configuration, leading to higher initial costs. Additionally, the maintenance and troubleshooting of these motors can be more challenging compared to regular induction motors.
Applications of Dual Speed Induction Motors
Dual speed induction motors find a wide range of applications across various industries. In HVAC systems, for instance, they are used to adjust the speed of fans and pumps based on environmental conditions, thereby improving energy efficiency. Similarly, in the manufacturing industry, they are used in conveyor systems, where the speed of the conveyor belt can be adjusted according to the operational requirements.
They are also used in applications where processes need different speeds at different times. For example, in a machine tool, slower speeds may be required for precise machining, and higher speeds may be needed for rough cutting. In such scenarios, the dual speed induction motor proves to be quite useful.
- Manufacturing Industry: For applications like conveyor belts, cranes, and lifts where speed control is essential.
- HVAC Systems: For controlling the speed of fans and pumps according to environmental conditions.
- Machine Tools: Where different machining processes require different speeds.
Maintenance of Dual Speed Induction Motors
Maintenance of dual speed induction motors is slightly more complex due to their dual winding configuration. It is essential to regularly check the condition of the windings and ensure the switches are operating correctly. The motor should also be kept clean, and the bearings should be lubricated regularly to ensure efficient operation.
Future of Dual Speed Induction Motors
With advancements in power electronics and control systems, the use of dual speed induction motors is expected to grow. Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) offer a more flexible way to control motor speed. However, dual speed induction motors remain a cost-effective solution for applications that require only two distinct speeds. The future developments in the design and control of these motors will continue to enhance their performance and efficiency, making them a viable choice for various industrial applications.
Conclusion
To conclude, dual speed induction motors offer a unique blend of simplicity and control, making them ideal for a wide range of applications. While they do come with their own set of challenges, such as increased complexity and higher initial costs, their advantages of speed control and energy efficiency often outweigh these drawbacks. As industries continue to seek cost-effective and energy-efficient solutions, the role of dual speed induction motors is set to become increasingly prominent. While future advancements in control systems may present new alternatives, the fundamental principle and benefits of these motors will continue to hold their ground in the realm of electromechanical energy conversion.

