Directional relays are protective devices that isolate faults in power systems by detecting the direction of fault currents.
Understanding Directional Relays: An Essential Component in Power System Protection
Introduction
Directional relays play a crucial role in the protection and control of power systems, ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of electrical networks. As an essential component in power system protection, they help to isolate faults and maintain the stability of the network. This article provides an in-depth overview of directional relays, their functions, and applications.
What is a Directional Relay?
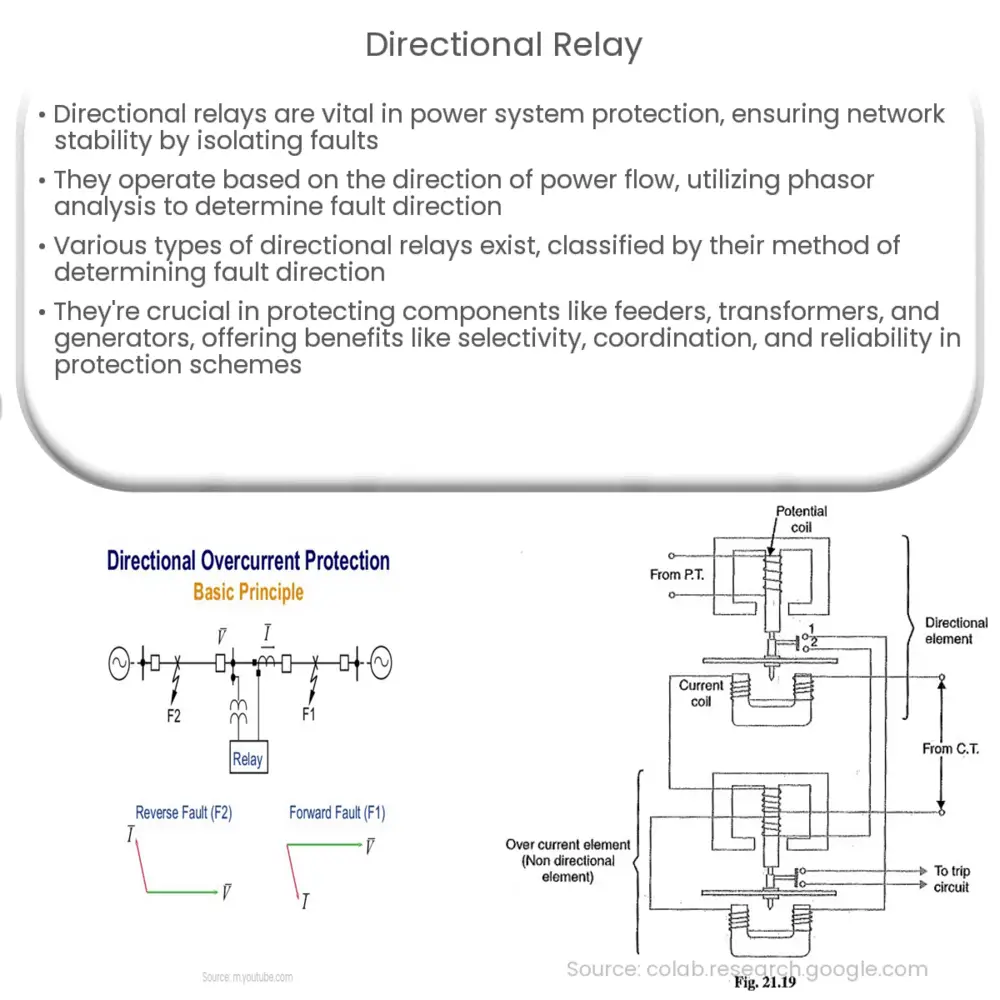
A directional relay is a type of protective relay that operates based on the direction of the power flow in an electrical circuit. It compares the direction of the fault current to a predetermined reference direction and, if the fault current is in the opposite direction of the reference, the relay operates to trip the appropriate circuit breaker. This functionality helps to isolate the faulty section of the network, minimizing disruptions and ensuring system stability.
Operating Principle of Directional Relays
Directional relays work based on the concept of phasor analysis. A phasor is a complex number that represents both the magnitude and phase angle of an alternating quantity, such as voltage or current. The relay compares the phase angle between the fault current and a reference voltage to determine the direction of the fault.
The reference voltage is usually derived from the system voltage, while the fault current is obtained from the line current transformer. The relay’s operating characteristic is defined by a specific angle, known as the relay’s polarizing angle. If the angle between the fault current and reference voltage is within the operating range defined by the polarizing angle, the relay operates to trip the circuit breaker and isolate the fault.
Types of Directional Relays
Directional relays are classified into several types based on the method used to obtain the reference voltage and the relay’s operating characteristic. The most common types of directional relays include:
- Overcurrent Directional Relays: These relays use the phase difference between the current and voltage to determine the direction of the fault. They are commonly used in power systems with radial or parallel feeders.
- Impedance Directional Relays: These relays compare the impedance of the circuit to a predetermined reference impedance to determine the direction of the fault. Impedance directional relays are used in distance protection schemes, which help protect transmission lines and transformers.
- Power Directional Relays: These relays use the active and reactive power components to determine the direction of the fault. They are typically applied in the protection of generators and synchronous motors.
Applications of Directional Relays
Directional relays are used in various applications within the power system to provide protection against different types of faults. Some of the primary applications include:
- Feeder Protection: Directional relays are used to protect radial and parallel feeders from faults such as short circuits, ground faults, and overloads. They help to quickly isolate the faulty section of the feeder, preventing damage to equipment and minimizing service disruptions.
- Transformer Protection: Directional relays are employed in transformer protection schemes to guard against internal faults and external faults on connected transmission lines. They work in conjunction with other protective devices, such as differential relays, to provide comprehensive protection to transformers.
- Generator Protection: In power generation systems, directional relays are used to protect generators from faults that may occur within the generator or on connected transmission lines. They ensure that faults are quickly isolated to prevent damage to the generator and maintain the stability of the power system.
- Busbar Protection: Directional relays can also be used in busbar protection schemes to detect and isolate faults within the busbar zone. They help to maintain the integrity of the power system by quickly disconnecting the faulty section from the rest of the network.
Advantages of Directional Relays
Directional relays offer several benefits in power system protection, including:
- Selectivity: Their ability to operate based on the direction of the fault current allows for improved selectivity in the protection scheme, minimizing the impact of faults on the power system.
- Coordination: Directional relays can be easily coordinated with other protective devices in the system, such as non-directional relays and circuit breakers, to provide comprehensive protection against various types of faults.
- Reliability: Due to their simple operating principle and well-established design, directional relays are considered highly reliable in detecting and isolating faults within the power system.
Conclusion
Directional relays are an essential component in power system protection, providing a reliable and efficient means of isolating faults and maintaining the stability of electrical networks. With their ability to determine the direction of fault currents and operate selectively, directional relays play a critical role in the protection of various power system components, such as feeders, transformers, generators, and busbars. Understanding their operating principles, types, and applications is essential for designing effective protection schemes in modern power systems.

