Explore the essentials of current regulators, their types, key components, applications, and challenges. Understand their role in modern electronics.
Understanding Current Regulators
A current regulator is a crucial component in electronics engineering. It serves to regulate or maintain a constant electrical current flowing through a circuit, despite variations in load resistance or input voltage. In essence, it prevents electrical devices from getting damaged due to inconsistent power supply.
Types of Current Regulators
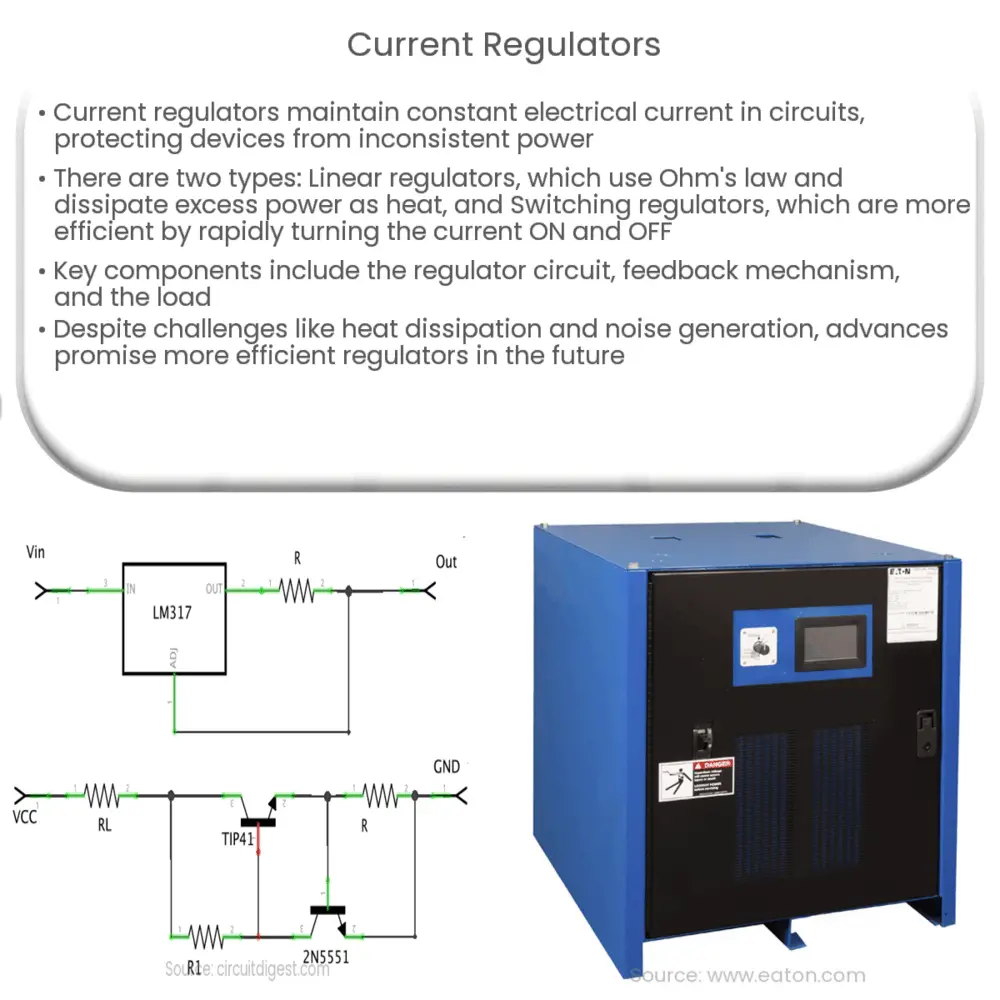
- Linear Current Regulators: These are simple devices that work on the principle of Ohm’s law. The resistance is adjusted to control the flow of current through the circuit. The excess power is dissipated as heat.
- Switching Current Regulators: These regulators operate by turning the supply current ON and OFF rapidly. The effective average current output is regulated by varying the duty cycle or the proportion of time the switch is ON. Unlike linear regulators, they don’t dissipate excess power as heat, making them more efficient.
Key Components of a Current Regulator
- Regulator Circuit: The central part of the current regulator, this circuit uses semiconductor devices such as diodes or transistors to regulate current flow.
- Feedback Mechanism: It is used to provide real-time adjustments to the regulator circuit. It measures the output current and adjusts the resistance of the regulator circuit as needed.
- Load: This represents the device or circuit that the current is supplied to. In a well-designed current regulator, the current supplied to the load should remain constant irrespective of changes in the load’s resistance.
Applications of Current Regulators
Current regulators are employed in numerous applications across various industries. They’re integral in power supplies, battery chargers, and LED drivers. In the telecommunication industry, they are used in power amplifiers, while in the automotive industry, they find use in DC-DC converters and fuel pumps.
Current Regulator Characteristics
Each type of current regulator has its unique characteristics. For instance, linear current regulators are simple and provide a clean output but are less efficient due to power loss in the form of heat. Switching regulators, on the other hand, are highly efficient but may produce noise in the circuit. Thus, the selection of a current regulator is largely dependent on the specific requirements of an application.
The Working Principle of Current Regulators
To gain a comprehensive understanding of current regulators, it’s essential to understand their working principle. A typical current regulator includes a voltage source, a variable resistor, and a sensing resistor. The sensing resistor measures the current flowing through the load and produces a voltage proportional to this current. This voltage is fed back to the control circuit, which adjusts the resistance of the variable resistor. As a result, the current is kept at a constant level.
Common Challenges with Current Regulators
- Heat Dissipation: Especially with linear current regulators, one of the main challenges is the heat generated due to the dissipation of excess power. This necessitates the use of heat sinks or cooling systems.
- Noise Generation: While switching current regulators are more efficient, they can produce electrical noise due to rapid switching. This can interfere with the operation of sensitive components in the circuit.
- Complex Design: Designing a current regulator requires a deep understanding of electrical engineering principles and can be complex, especially for high-power applications.
Future of Current Regulators
The future of current regulators is intertwined with the continual evolution of electronics. The demand for higher efficiency, smaller size, and lower cost is driving innovation in this area. New materials and technologies, such as wide bandgap semiconductors and digital control techniques, are being explored to create the next generation of current regulators.
Conclusion
In conclusion, current regulators are indispensable in modern electronics, playing a pivotal role in maintaining a stable power supply to numerous devices. Despite their challenges, including heat dissipation and noise generation, ongoing technological advances promise to deliver more efficient and compact current regulators. Whether for use in telecommunications, automotive systems, or consumer electronics, understanding current regulators is a fundamental aspect of electronics engineering. As we continue to strive for improved efficiency and innovation, current regulators will undoubtedly continue to evolve, proving integral to our technology-driven future.

