Current-limiting diodes (CLDs) are semiconductor devices that regulate and maintain a constant current flow, protecting sensitive electronics.
Understanding Current-Limiting Diodes (CLDs): An Essential Component in Electronics
Introduction to Current-Limiting Diodes
Current-limiting diodes (CLDs) are a crucial component in electronic circuits, responsible for protecting sensitive devices from excessive current flow. Also known as constant-current diodes or current-regulating diodes, these semiconductor devices enable the precise control of current in a circuit, ensuring the smooth operation of electronic equipment and preventing damage from overcurrent events. In this article, we will explore the principles, applications, and benefits of CLDs in modern electronics.
How Current-Limiting Diodes Work
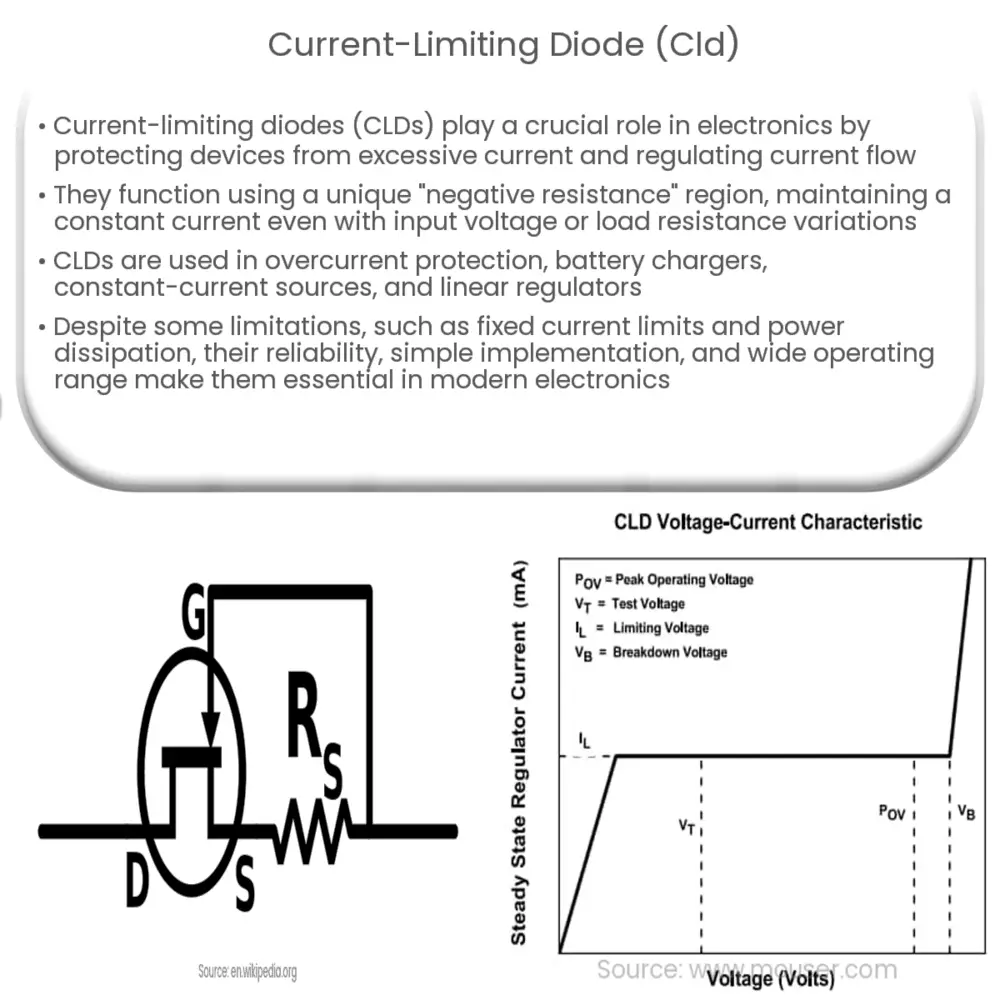
A CLD operates based on the properties of a semiconductor junction, typically formed by a p-n junction. When a voltage is applied across the diode, it allows current to flow in the forward direction (from the anode to the cathode) but restricts the current flow in the reverse direction. The CLD functions by maintaining a constant current through the device, regardless of variations in the input voltage or load resistance.
This behavior is achieved through a unique characteristic of the diode called the “negative resistance” region. As the voltage across the diode increases, the current initially increases until it reaches a specific threshold value known as the “knee” point. Beyond this point, any further increase in voltage results in a decrease in current. This self-regulating feature enables the CLD to maintain a constant current, effectively limiting the current flow in the circuit to a predefined value.
Applications of Current-Limiting Diodes
CLDs find a wide range of applications in various electronic systems, including:
- Overcurrent protection: CLDs are often employed to protect sensitive electronic components, such as microprocessors, from damage due to excessive current flow. By maintaining a constant current, they prevent harmful overcurrent events from occurring, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the electronic devices.
- Constant-current sources: CLDs can be used to create constant-current sources for applications such as LED lighting, where maintaining a stable current is critical for consistent brightness and longevity of the light-emitting diodes.
- Battery chargers: In battery charging applications, CLDs can be used to limit the charging current, preventing damage to the batteries from overcharging and ensuring a safe charging process.
- Linear regulators: CLDs can be incorporated in linear regulator circuits to provide a stable output current, regardless of variations in input voltage or load resistance, improving the overall performance and efficiency of the regulator.
Advantages of Current-Limiting Diodes
CLDs offer several benefits in electronic circuit design, such as:
- Simple implementation: CLDs require minimal external components, making them easy to integrate into a circuit. Their small size and straightforward operation help simplify the overall design process.
- High reliability: Due to their inherent self-regulating properties, CLDs provide a high degree of reliability in maintaining a constant current flow. This reduces the risk of component failure and increases the lifespan of the electronic devices they protect.
- Wide operating range: CLDs can function over a broad range of voltages and temperatures, making them suitable for use in various environments and applications.
- Fast response time: CLDs exhibit a rapid response to changes in input voltage or load resistance, ensuring that the current regulation remains stable and accurate even under dynamic conditions.
Limitations of Current-Limiting Diodes
While CLDs offer numerous advantages, they also have some limitations:
- Fixed current limit: CLDs are typically designed with a predefined current limit, which may not be adjustable or customizable for specific applications. This can limit their flexibility in certain use cases.
- Power dissipation: In high-voltage applications, CLDs can generate a significant amount of heat due to their power dissipation, which may necessitate the use of additional heat management solutions, such as heatsinks.
- Accuracy: The current regulation accuracy of a CLD may vary depending on factors such as temperature, manufacturing tolerances, and input voltage. This may require additional calibration or compensation in certain applications to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
Current-limiting diodes (CLDs) are an essential component in modern electronics, providing critical protection and precise current regulation for various applications. Their simple implementation, high reliability, and wide operating range make them an attractive choice for designers seeking to optimize circuit performance and safeguard sensitive devices. Despite some limitations, CLDs remain a popular and effective solution for managing current flow in electronic circuits, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a wide range of electronic systems.

