Explore the basics of charge amplifiers, their components, benefits, and applications in various industries. Dive into the world of signal processing.
Understanding Charge Amplifiers
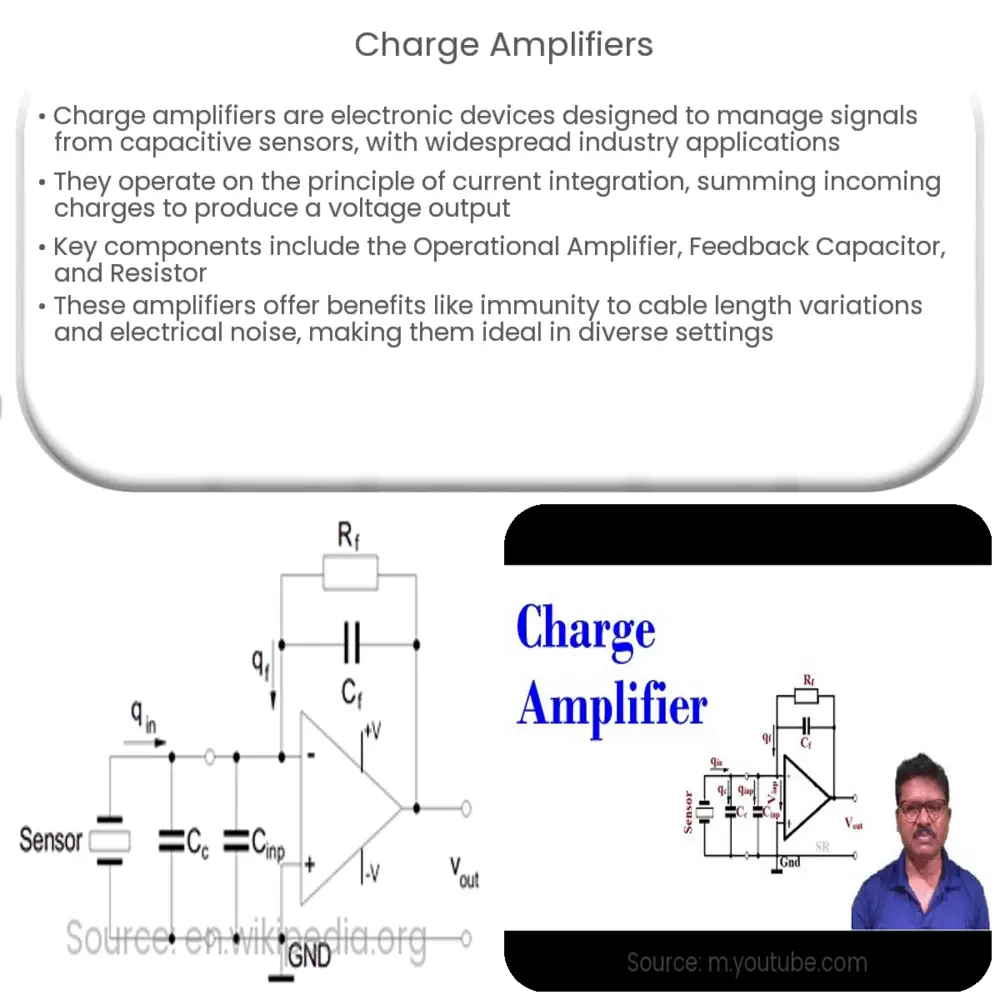
A charge amplifier is an electronic device that is designed to integrate an incoming current, convert it into a proportional voltage, and output this signal. The primary function of charge amplifiers is to manage signals from capacitive sensors such as piezoelectric sensors, photodiodes, or condenser microphones. Its purpose and functionality are fundamental in various applications across several industries including automotive, aerospace, industrial processes, and more.
The Basic Principle
At its core, a charge amplifier operates on the principle of current integration. To put it simply, it sums up all the incoming electric charges from a capacitive transducer to generate a voltage output. This voltage is then held across the feedback capacitor, Cf, thereby creating a very low impedance input.
The output voltage Vo is given by the formula Vo = -Q/Cf, where Q represents the total incoming charge. The negative sign implies an inversion in the phase of the output signal compared to the input.
Key Components of a Charge Amplifier
- Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp): This is the heart of the charge amplifier. It amplifies the input signal and drives the output signal.
- Feedback Capacitor (Cf): This component is placed between the output and input of the op-amp. The charge generated by the sensor is stored in Cf.
- Resistor (Rf): The resistor Rf is connected parallel to Cf. This part is responsible for the reset mechanism of the amplifier and determines the discharge time constant, which affects the response time of the system.
Performance Parameters
There are several critical performance parameters to consider when dealing with charge amplifiers. These include Gain Stability, Linearity, and Bandwidth. Each parameter is crucial in determining how efficiently and effectively a charge amplifier operates, and they can greatly affect the quality and reliability of the amplified signal.
The amplifier’s output signal depends on the total incoming charge and the feedback capacitor’s value, which means the output is essentially independent of the input impedance. This makes the charge amplifier particularly effective in dealing with capacitive sensors, as they are not affected by cable length or the sensor’s capacitance.
Benefits of Charge Amplifiers
Charge amplifiers come with numerous benefits that make them highly valuable in many applications. One of the key advantages is their immunity to cable length variations, which allows for flexibility in equipment setup. Moreover, they are not affected by the varying cable capacitance, which could distort the signal in other amplifier designs.
The low impedance input of the charge amplifier also results in high immunity to electrical noise. This property makes charge amplifiers ideal for use in electrically noisy environments, such as industrial settings, where reliable signal transmission is vital.
Applications of Charge Amplifiers
Charge amplifiers play an essential role in several applications:
- Piezoelectric Sensors: These sensors generate a charge proportional to the force applied to them. A charge amplifier can be used to convert this charge into a usable voltage signal.
- Photodiodes: Photodiodes, when exposed to light, produce a current proportional to the light intensity. Charge amplifiers can be used to convert this current into a voltage signal.
- Condenser Microphones: These microphones function based on changes in capacitance. A charge amplifier can convert these changes into a corresponding voltage signal.
Conclusion
In conclusion, charge amplifiers are integral components in the world of electronics and signal processing. Their unique ability to convert charge into a proportional voltage signal, combined with their robustness against variations in cable length and noise interference, makes them a preferred choice in many applications. From piezoelectric sensors to photodiodes and condenser microphones, the versatility and functionality of charge amplifiers underscore their significance in both industrial and consumer applications. As technology continues to advance, the role of charge amplifiers is expected to expand, facilitating more complex and innovative applications across various sectors.

