Explore the world of Carbon Film Resistors, their construction, applications, benefits, and limitations in our comprehensive guide.
Introduction to Carbon Film Resistors
A Carbon Film Resistor is an integral component in many electronic devices. These components are designed to limit the flow of electricity within circuits, a role that is essential for the smooth functioning of electronic devices. Let’s delve deeper to understand their nature, construction, and application.
The Nature of Carbon Film Resistors
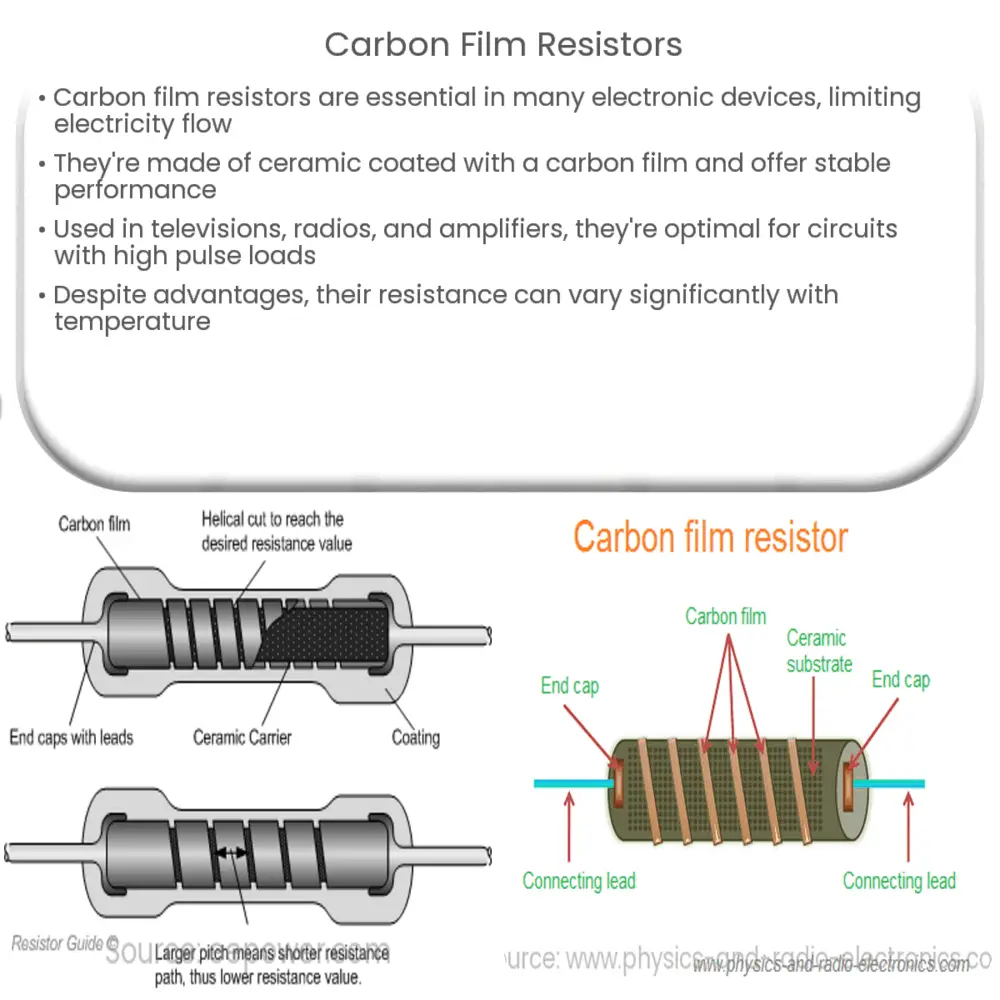
Carbon film resistors are a type of fixed form resistor. They are constructed out of a ceramic carrier coated with a thin layer of carbon. The name of these resistors is derived from this carbon layer, which is indeed a film, therefore, they are called ‘Carbon Film Resistors’. They are often used when a substantial amount of power dissipation is not required.
Construction of Carbon Film Resistors
The construction of a carbon film resistor begins with a ceramic substrate. This substrate is then coated with a layer of pure carbon film. This carbon film serves as the resistive material. By controlling the thickness and length of the carbon film, the desired resistance value can be achieved. The resistor is then encapsulated in a protective coating to enhance its durability and stability.
Applications of Carbon Film Resistors
-
They are widely used in the electronics industry due to their stable performance characteristics.
-
Carbon film resistors find their application in various devices such as televisions, radios, and amplifiers.
-
They are often used in circuits where a high pulse load is present.
Advantages of Carbon Film Resistors
-
Carbon film resistors have a high resistance per unit length as compared to other types of resistors.
-
The manufacturing process of carbon film resistors is simpler and less expensive than that of other types of resistors, making them a cost-effective option for many electronic applications.
-
These resistors are less susceptible to noise, which makes them suitable for use in sensitive electronic devices.
This provides a general overview of carbon film resistors. In the next section, we’ll explore more about their limitations, how they differ from other types of resistors, and additional applications.
Limitations of Carbon Film Resistors
While carbon film resistors have many advantages, they also come with their set of limitations:
-
The temperature coefficient of carbon film resistors is typically high, which means their resistance changes significantly with temperature. This could impact the overall performance of the circuit they are integrated into.
-
They are not as stable as metal film or wirewound resistors, making them less suitable for applications requiring high precision.
Difference Between Carbon Film and Other Types of Resistors
There are several types of resistors available, including carbon film, metal film, wirewound, and more. Each of these types has its own set of characteristics:
-
Compared to metal film resistors, carbon film resistors are less accurate and have a higher temperature coefficient, which can affect their stability.
-
Wirewound resistors, on the other hand, can handle a higher power load than carbon film resistors. However, they are more expensive and are usually used in applications where high power dissipation is required.
Additional Applications of Carbon Film Resistors
As we delve deeper into the electronics industry, the use of carbon film resistors is not limited to just televisions, radios, and amplifiers. They can also be found in:
-
Power supply units, limiting current and providing load to unused sections of the circuit.
-
Voltage regulators, providing a fixed load to the regulator for consistent output.
-
Pulse circuits, where the resistor needs to withstand high pulse loads.
Conclusion
In conclusion, carbon film resistors play a vital role in the electronics industry due to their cost-effectiveness, high resistance per unit length, and noise reduction capabilities. Despite certain limitations like high temperature coefficient and stability issues, they remain a popular choice in many applications ranging from everyday household appliances to more complex electronic circuits. Understanding their properties, strengths, and limitations is crucial for anyone involved in electronic design and manufacturing.

