Explore the functionality, types, applications, advantages, and disadvantages of buck-boost converters in power electronics and renewable energy systems.
Introduction to Buck-Boost Converters
A buck-boost converter is a type of DC-to-DC power converter that has an output voltage magnitude that can be greater than or less than the input voltage magnitude. It is equivalent to a flyback converter using a single inductor instead of a transformer.
Two different topologies are called buck–boost converter. Both of them can produce a range of output voltages, ranging from much larger (in absolute magnitude) than the input voltage, down to almost zero.
Working Principle of Buck-Boost Converters
The primary principle behind the buck-boost converter is the tendency of an inductor to resist changes in current. When the switch in the converter is turned on, current flows through the inductor in one direction, and the inductor stores some energy by generating a magnetic field. When the switch is opened, the current will want to continue flowing in the same direction, and so it will flow to the load. As a result, the polarity of the output voltage is inverted.
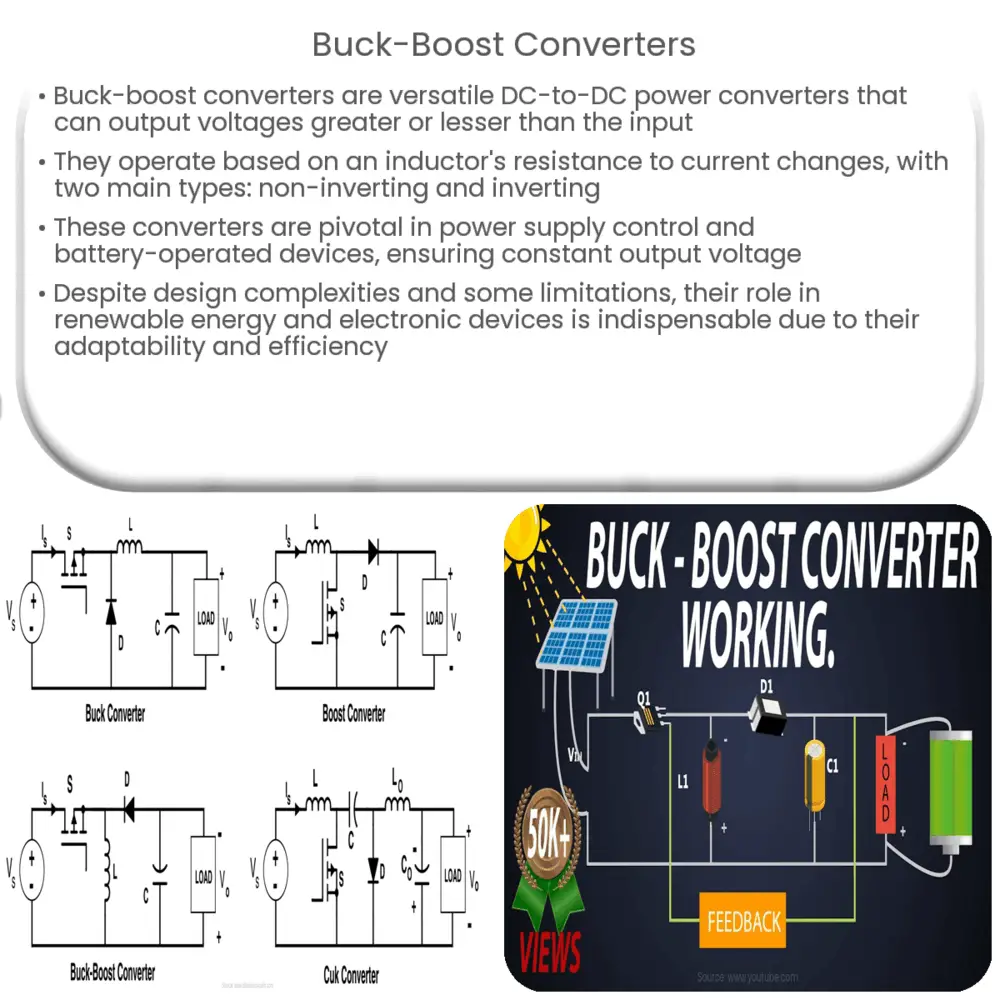
Types of Buck-Boost Converters
- Non-inverting Buck-Boost Converter: In a non-inverting buck-boost converter, the output voltage is of the same polarity as the input. This type of converter is a combination of the buck converter and the boost converter with a common ground. But it has one limitation: it cannot produce an output voltage range that’s between the input voltage and zero.
- Inverting Buck-Boost Converter: The output voltage polarity of an inverting buck-boost converter is opposite to the input voltage. This is a more traditional type of buck-boost converter.
Applications of Buck-Boost Converters
- Power Supply Control: Buck-boost converters are commonly used in power supply control. They ensure that even if the input voltage varies, the output voltage remains constant. They can step up or step down voltages as per the requirement.
- Battery Operated Devices: These converters are often found in battery-operated devices such as smartphones, laptops, and portable music players. They provide a constant power supply to the device, even as the battery voltage changes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Buck-Boost Converters
- Advantages: The main advantage of a buck-boost converter is its versatility. It can increase or decrease voltage as needed, which is beneficial in various applications. Moreover, it’s capable of maintaining a steady output voltage despite changes in the input voltage, thus providing high efficiency and excellent response to load changes.
- Disadvantages: Despite these benefits, buck-boost converters do come with some drawbacks. The design and implementation can be complex, especially for systems requiring high power and efficiency. Furthermore, they generate output voltage with reverse polarity, which could be a limitation in certain applications.
Buck-Boost Converters in Renewable Energy Systems
With the rise of renewable energy, the application of buck-boost converters has expanded significantly. In solar power systems, for instance, they can regulate the voltage output from solar panels to match the required input of the battery or grid.
In wind energy systems, buck-boost converters can maximize the power output by adjusting the voltage and current according to the varying speed of the wind. Similarly, in electric vehicles, they control the power flow between the battery, the motor, and other electrical components.
Conclusion
In conclusion, buck-boost converters play an essential role in modern electronic devices and renewable energy systems due to their ability to adjust voltage levels according to the requirements. Their efficiency, versatility, and wide range of applications make them a fundamental component of power electronics. While they do have some drawbacks, such as complexity in design and implementation, the benefits far outweigh these challenges. As technology continues to advance, it is anticipated that further improvements and variations of the buck-boost converter will emerge, offering even greater efficiency and adaptability.

