Explore the workings, types, advantages, and applications of AC motors, their key components, control methods, and future prospects.
Introduction to Alternating Current (AC) Motors
Alternating Current (AC) motors are a critical type of electric motor, essential for many applications in various industries. These motors utilize alternating current to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, which then drives the device or machinery.
Principle of Operation
The fundamental principle behind AC motors revolves around the idea of electromagnetism. When electric current flows through a wire, it generates a magnetic field. This property is used in the construction of AC motors, where a magnetic field interacts with the current in the motor windings to produce a force – this force, in turn, results in motion.
Types of AC Motors
- Induction Motors: Also known as asynchronous motors, they are the most common type of AC motor. Induction motors depend on a simple electromagnetic principle, creating a rotating magnetic field with the AC current. The rotor in the motor does not receive any direct power but instead, it gets induced by the magnetic field.
- Synchronous Motors: Unlike induction motors, the rotor turns at the same speed as the stator’s magnetic field in synchronous motors. These motors require additional starting mechanisms to reach the synchronous speed and start operating.
- Servo Motors: These motors are specifically designed for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration. They are commonly used in robotics, CNC machinery, and automated manufacturing.
Advantages of AC Motors
AC motors have many advantages that have contributed to their widespread use:
- They are relatively simple in design and robust in nature, resulting in lower maintenance and longer lifespans.
- The speed of AC motors can be controlled over a wide range, providing flexibility in operation.
- They are more efficient in terms of power consumption compared to DC motors.
- AC motors do not require any starters as they can directly run on the supply voltage.
Applications of AC Motors
AC motors find extensive applications in various sectors. In industrial applications, they are used in fans, pumps, conveyors, and machine tools. Other common applications include appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners, which all use AC motors in their functioning.
Disadvantages of AC Motors
Despite their numerous advantages, AC motors also come with a few downsides:
- One major drawback is that controlling the speed of AC motors is more complex compared to DC motors.
- Additionally, AC motors produce a significant amount of noise and heat, which may require additional cooling systems in certain applications.
- Lastly, they cannot provide high starting torque as compared to DC motors.
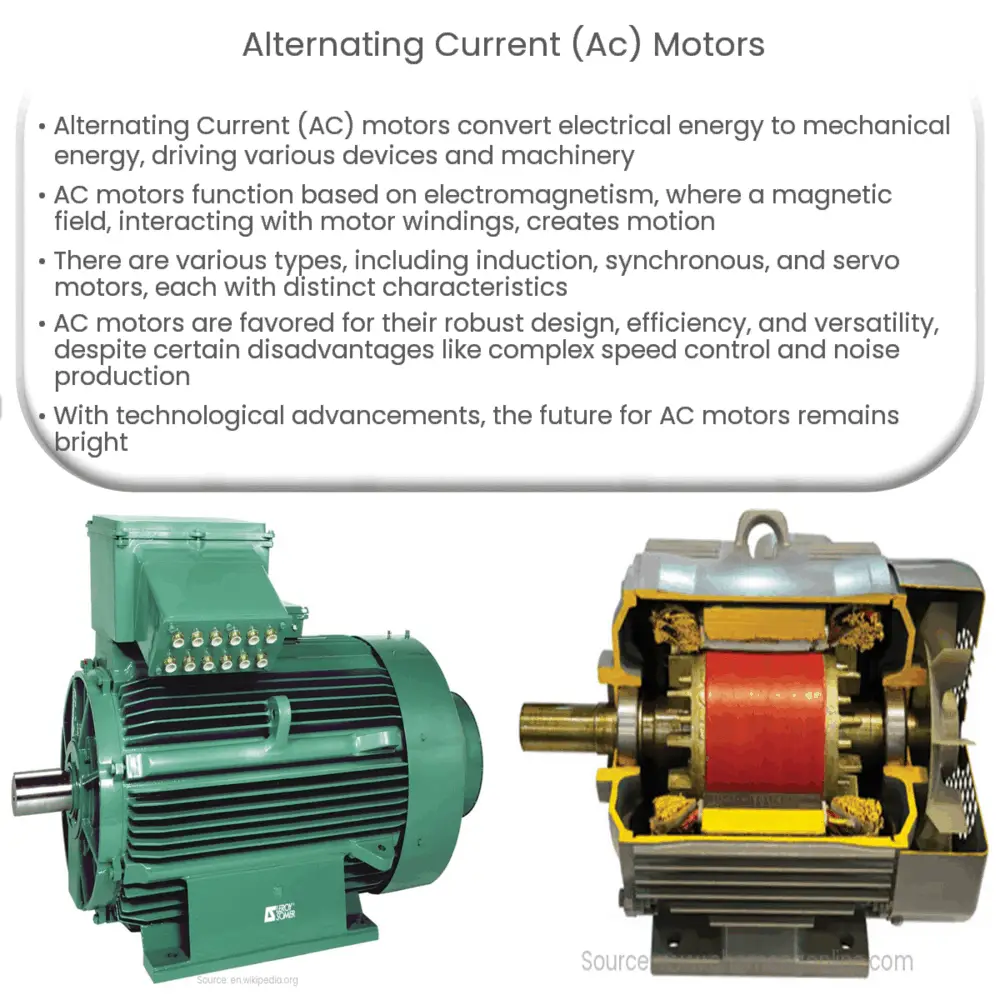
Key Components of AC Motors
AC motors typically consist of two main components:
- The Stator: This is the stationary part of the motor, which includes windings connected to a power source. The stator creates a rotating magnetic field when AC power is applied.
- The Rotor: The rotor is the rotating part of the motor. In response to the magnetic field produced by the stator, the rotor spins, converting the electrical energy into mechanical energy.
AC Motor Control
Control methods for AC motors have advanced significantly over the years. Modern AC motors are often paired with variable frequency drives (VFDs) to control the motor’s speed and torque. VFDs adjust the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor, giving operators precise control over the motor’s performance.
Future of AC Motors
With the increasing trend towards energy efficiency and automation, the future of AC motors looks promising. Advancements in motor design and control methods are expected to make AC motors even more efficient, reliable, and versatile.
Conclusion
In conclusion, AC motors play an essential role in modern industries and households. Their ability to efficiently convert electrical energy into mechanical energy makes them invaluable for a wide array of applications. Despite some disadvantages, the advantages of AC motors like simple design, low maintenance, and high efficiency often outweigh their limitations. With continued technological advancements and an increasing emphasis on energy efficiency, the usage and importance of AC motors are only expected to grow in the future.

