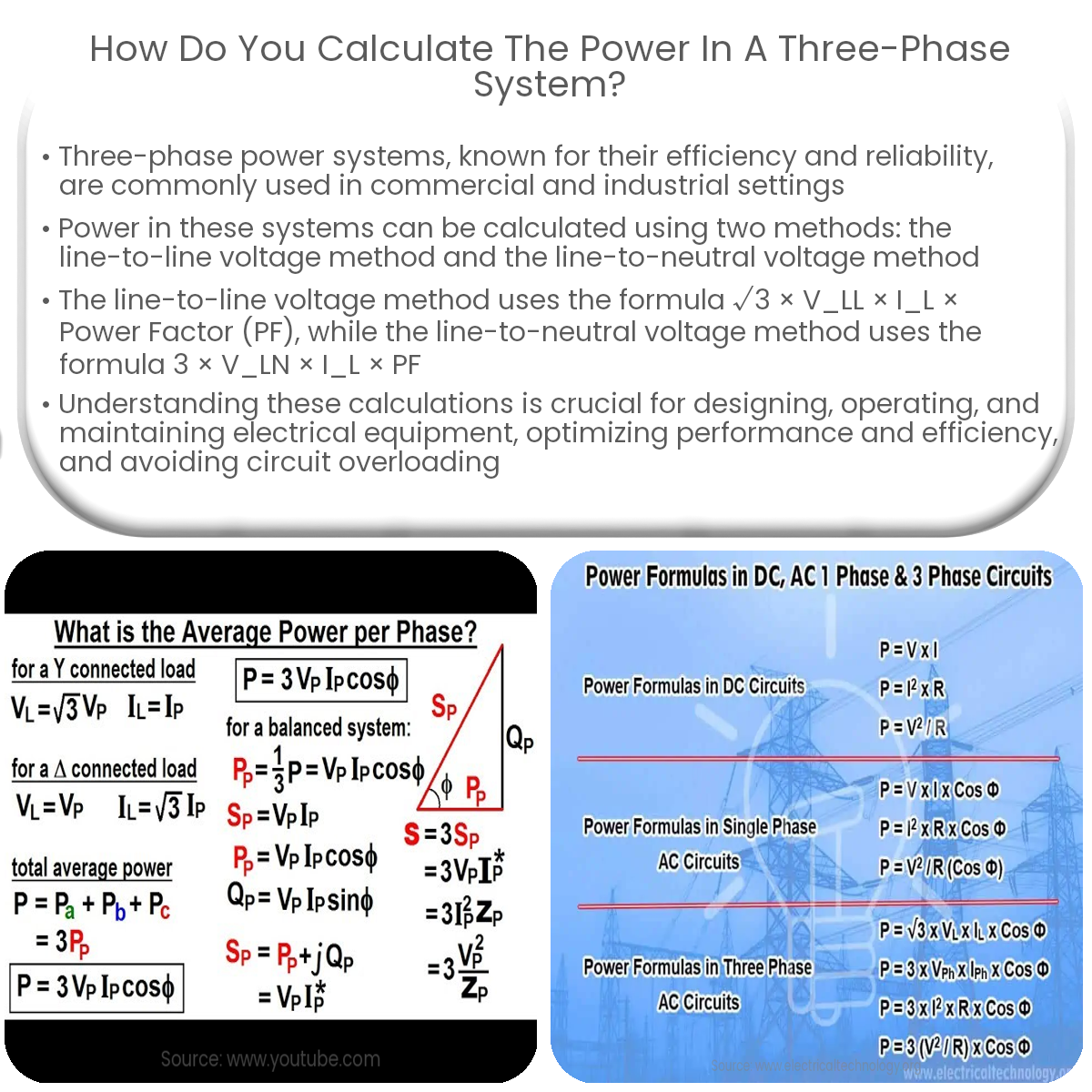
Calculate three-phase power using Pₜ = √3 × Vₗₗ × Iₗ × PF or Pₜ = 3 × Vₗₙ × Iₗ × PF, depending on the available voltage and current values.
Calculating Power in a Three-Phase System
Three-phase power systems are widely used in commercial and industrial applications due to their efficiency and reliability. Calculating the power in a three-phase system is essential for designing, operating, and maintaining electrical equipment. This article will explain how to calculate the power in a three-phase system using two different methods: the line-to-line voltage method and the line-to-neutral voltage method.
Line-to-Line Voltage Method
The line-to-line voltage method is used when the line-to-line voltage (VLL) and the line current (IL) are known. The formula for calculating the total power (PT) in a balanced three-phase system using the line-to-line voltage method is:
PT = √3 × VLL × IL × Power Factor (PF)
Where:
- VLL is the line-to-line voltage
- IL is the line current
- PF is the power factor, which is a dimensionless number between -1 and 1, representing the phase angle between voltage and current
Line-to-Neutral Voltage Method
The line-to-neutral voltage method is used when the line-to-neutral voltage (VLN) and the line current (IL) are known. The formula for calculating the total power (PT) in a balanced three-phase system using the line-to-neutral voltage method is:
PT = 3 × VLN × IL × Power Factor (PF)
Where:
- VLN is the line-to-neutral voltage
- IL is the line current
- PF is the power factor
Example Calculation
Suppose you have a balanced three-phase system with a line-to-line voltage of 480 V, a line current of 50 A, and a power factor of 0.8. Using the line-to-line voltage method, the total power can be calculated as follows:
PT = √3 × 480 V × 50 A × 0.8 = 33,177.48 W or 33.18 kW
Applications and Importance
Calculating the power in a three-phase system is crucial for various applications, including:
- Designing electrical systems for commercial and industrial installations
- Monitoring and controlling power consumption
- Optimizing equipment performance and efficiency
- Ensuring proper load balancing and avoiding overloading of electrical circuits
By understanding how to calculate the power in a three-phase system, engineers and technicians can effectively design, operate, and maintain electrical equipment in commercial and industrial settings.