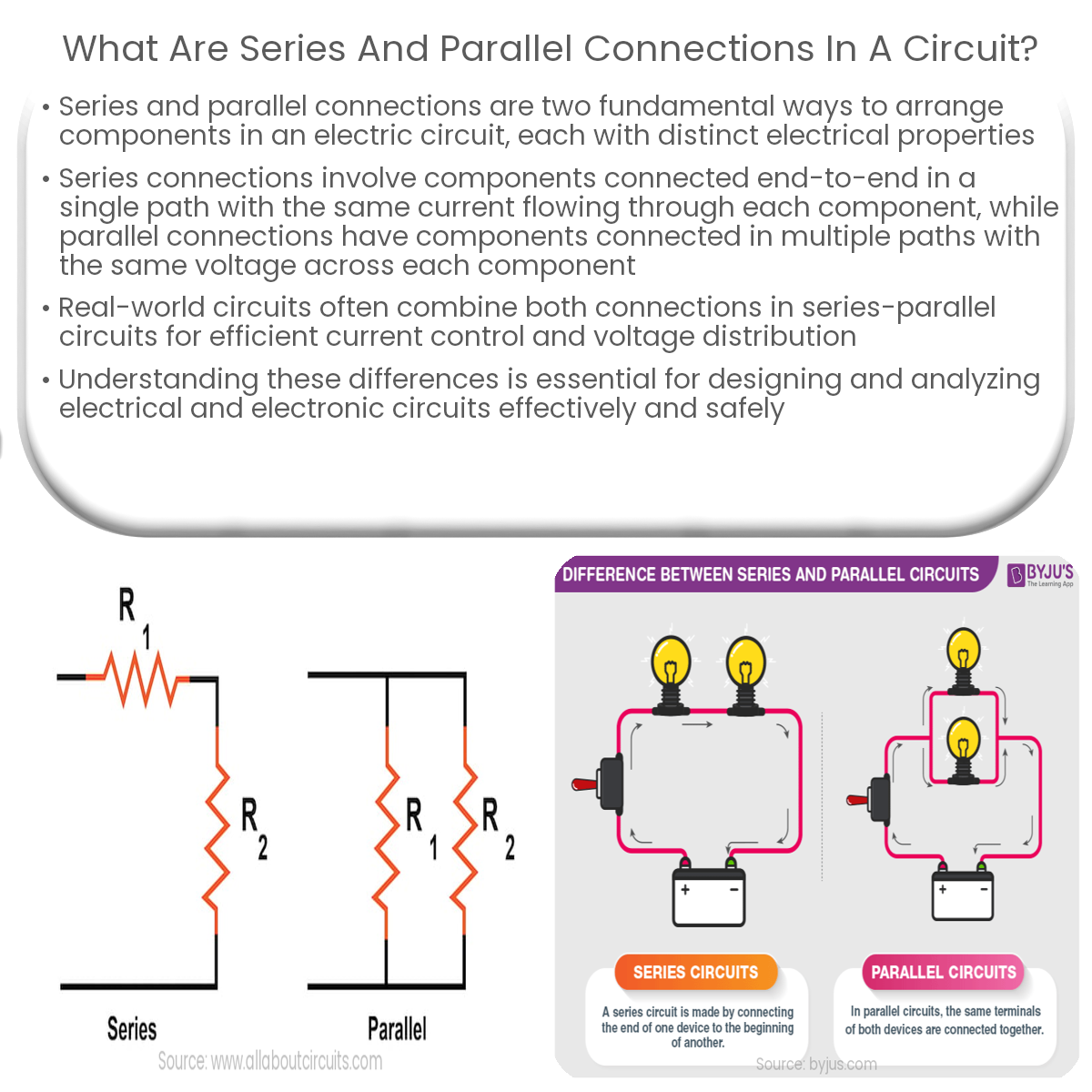
Series connections have components in a single path with equal current, while parallel connections have multiple paths with equal voltage across them.
Series and Parallel Connections in a Circuit
Series and parallel connections are two fundamental ways to arrange components in an electric circuit. These configurations have different electrical properties and are used to achieve specific purposes in the design of electrical and electronic systems.
Series Connection
In a series connection, components are connected end-to-end in a single path so that the current flows through each component sequentially. The total resistance of the circuit is the sum of the individual resistances:
Rtotal = R1 + R2 + … + Rn
One notable characteristic of a series connection is that the current flowing through each component is the same. However, the voltage across each component may differ depending on the resistance values.
Parallel Connection
In a parallel connection, components are connected in multiple paths, with each path connected directly to the voltage source. This allows the current to flow simultaneously through all paths. The total resistance of a parallel circuit is calculated using the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of individual resistances:
1/Rtotal = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + … + 1/Rn
Unlike a series connection, the voltage across each component in a parallel connection is the same. However, the current flowing through each path may differ depending on the resistance values.
Combining Series and Parallel Connections
Real-world circuits often use a combination of series and parallel connections to control the flow of current and distribute voltage efficiently. These mixed configurations, called series-parallel circuits, can be analyzed by breaking them down into simpler series and parallel sections and applying the appropriate equations.
Applications
-
Series connections are commonly used in applications where a specific current value is needed across multiple components, such as in LED lighting circuits.
-
Parallel connections are often used in power distribution systems to ensure a consistent voltage supply across multiple devices or branches, such as in household electrical wiring.
Understanding the differences between series and parallel connections is crucial for designing and analyzing electrical and electronic circuits efficiently and safely.