Capacitive proximity sensors detect object presence, distance, or position using capacitance changes, ideal for various industrial applications.
Capacitive Proximity Sensors: Understanding the Basics and Applications
Introduction
Capacitive proximity sensors are widely used in various industries for detecting and measuring the presence, distance, or position of objects. They have become increasingly popular due to their non-contact nature, which ensures minimal wear and tear on the sensors and the objects being detected. In this article, we will explore the basic principles of capacitive proximity sensors, how they work, and their most common applications.
How Capacitive Proximity Sensors Work
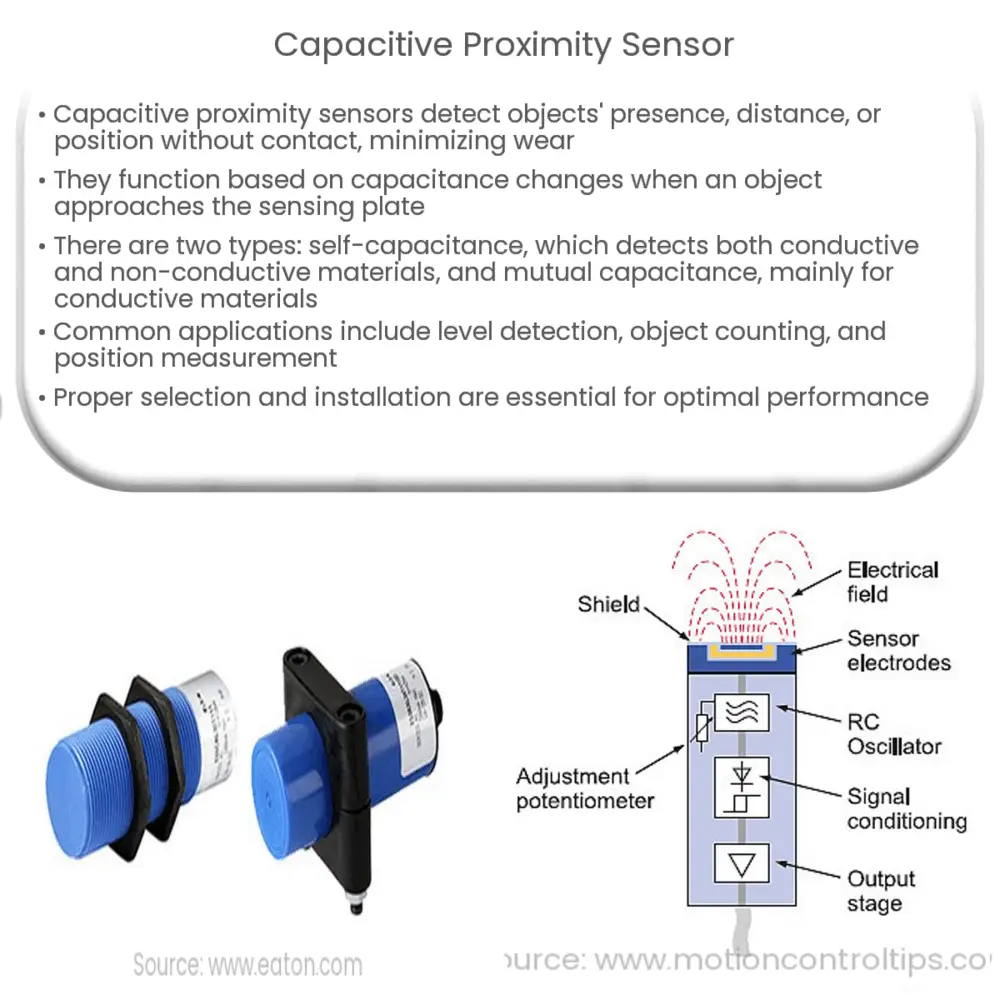
Capacitive proximity sensors operate on the principle of capacitance, which is the ability of a system to store an electric charge. The sensor consists of an oscillator circuit, a sensing plate, and a detection circuit. The sensing plate, often made of conductive materials such as metal or conductive plastic, acts as one electrode of a capacitor. When an object, either conductive or non-conductive, comes near the sensing plate, it acts as the second electrode, creating a change in the capacitance of the system. This change is then detected by the detection circuit, which sends a signal to indicate the presence or absence of the target object.
Types of Capacitive Proximity Sensors
There are two primary types of capacitive proximity sensors: self-capacitance and mutual capacitance sensors.
Self-Capacitance Sensors
Self-capacitance sensors measure the capacitance between the sensing plate and the target object. As the object approaches the sensing plate, the capacitance increases, causing a change in the oscillation frequency of the sensor’s internal oscillator circuit. The detection circuit then measures this frequency change and sends an output signal when the change exceeds a predefined threshold. Self-capacitance sensors are suitable for detecting both conductive and non-conductive materials, making them versatile for various applications.
Mutual Capacitance Sensors
Mutual capacitance sensors, on the other hand, measure the capacitance between two adjacent sensing plates. When an object comes near the sensor, it causes a change in the mutual capacitance between the plates. This change is then detected by the detection circuit and used to determine the presence or position of the target object. Mutual capacitance sensors are more sensitive than self-capacitance sensors but are primarily used for detecting conductive materials.
Applications of Capacitive Proximity Sensors
Capacitive proximity sensors have a wide range of applications in various industries. Some of the most common applications include:
- Level detection: Capacitive sensors are often used to detect the presence or absence of liquids, granules, or powders in containers or tanks.
- Object counting: Sensors can be used to count objects passing through a production line, ensuring accurate inventory management and quality control.
- Position and distance measurement: Capacitive sensors can be used to measure the distance between an object and the sensor or to determine the position of an object in a predefined area.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Capacitive Proximity Sensors
Capacitive proximity sensors offer several advantages, including:
- Non-contact detection: Since these sensors do not require physical contact with the target object, they experience minimal wear and tear, resulting in a longer service life.
- Versatility: Capacitive sensors can detect both conductive and non-conductive materials, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Resistance to environmental factors: Many capacitive sensors are designed to withstand harsh environments, including dust, dirt, and moisture.
However, capacitive proximity sensors also have some disadvantages:
- Sensitivity to interference: Capacitive sensors can be affected by electromagnetic interference (EMI) or radio frequency interference (RFI), which may cause false detections or reduce sensing range.
- Limited sensing range: Compared to other types of sensors, capacitive sensors generally have a shorter sensing range, typically limited to a few millimeters or centimeters.
Selection and Installation Tips
When choosing a capacitive proximity sensor for a specific application, consider the following factors:
- Sensing range: Ensure the sensor’s sensing range is appropriate for the application’s requirements.
- Target material: Choose a sensor that is compatible with the material properties of the target object, such as its conductivity and dielectric constant.
- Environmental conditions: Select a sensor designed to withstand the specific environmental conditions of the application, including temperature, humidity, and the presence of dust or moisture.
- Mounting and installation: Consider the sensor’s mounting and installation requirements, such as the available space and any necessary mounting brackets or hardware.
Proper installation of capacitive proximity sensors is essential for optimal performance. Some installation tips include:
- Avoid installing sensors near sources of EMI or RFI, which can interfere with the sensor’s performance.
- Ensure that the sensor’s sensing plate is clean and free of debris or contaminants, as these can affect the sensor’s accuracy and sensitivity.
- Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for mounting and wiring the sensor, paying close attention to any grounding or shielding requirements.
Conclusion
Capacitive proximity sensors are valuable tools for detecting and measuring the presence, distance, or position of objects in various industries. Their non-contact nature, versatility, and resistance to environmental factors make them a popular choice for many applications. By understanding the basics of how capacitive sensors work, their advantages and disadvantages, and proper selection and installation, users can optimize their performance and ensure the success of their sensing applications.

