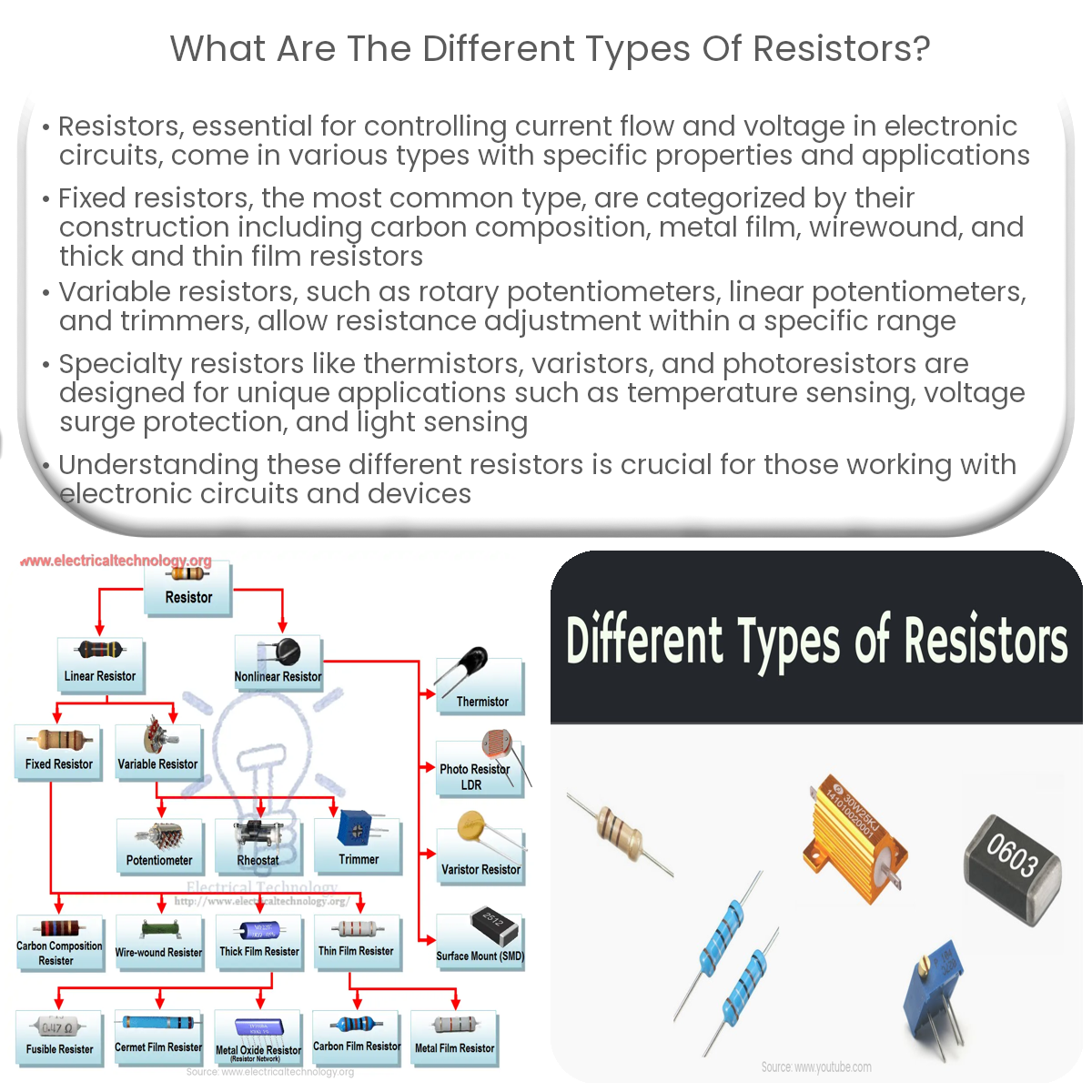
Resistors come in various types like fixed, variable, and specialty, each designed for specific purposes such as current control, voltage reduction, or sensing.
Types of Resistors
Resistors are essential components in electronic circuits, used for controlling current flow, voltage reduction, and protecting sensitive components. There are various types of resistors, each with its specific properties and applications. This article discusses the most common types of resistors and their uses.
Fixed Resistors
Fixed resistors have a constant resistance value and are the most common type of resistor. They are typically categorized by their construction:
- Carbon Composition: Composed of a mixture of carbon and an insulating binder, these resistors are inexpensive and suitable for general-purpose applications.
- Metal Film: Featuring a thin metal film deposited on an insulating substrate, metal film resistors offer better accuracy, stability, and lower noise compared to carbon composition resistors.
- Wirewound: Made by winding a metal wire, usually nichrome, around an insulating core, wirewound resistors can handle high power and are used in applications requiring precision and stability.
- Thick and Thin Film: These resistors are made by depositing a resistive film on a ceramic substrate, either by screen printing (thick film) or vapor deposition (thin film). They offer high precision and stability.
Variable Resistors
Variable resistors, also known as potentiometers or rheostats, allow the adjustment of resistance within a certain range. Common types include:
- Rotary Potentiometer: A rotary potentiometer uses a rotating contact to adjust the resistance value. It is commonly used for volume control in audio equipment.
- Linear Potentiometer: Linear potentiometers have a sliding contact that moves along a straight resistive track, typically used in position sensing applications.
- Trimmer: Trimmers are small, adjustable resistors designed for infrequent or one-time adjustments, often used for fine-tuning circuits.
Specialty Resistors
Some resistors have unique properties for specific applications:
- Thermistors: Thermistors are resistors whose resistance changes with temperature. They can be used for temperature sensing, compensation, and control.
- Varistors: Varistors exhibit a non-linear resistance that changes with voltage, providing surge protection in power supplies and other electronic devices.
- Photoresistors: Also known as light-dependent resistors (LDRs), photoresistors change their resistance based on the amount of light they receive, making them ideal for light-sensing applications.
Conclusion
Resistors come in various types, each with specific properties and applications. Fixed resistors are categorized by their construction, while variable resistors allow for resistance adjustment. Specialty resistors are designed for specific purposes, such as temperature sensing, voltage surge protection, or light sensing. Understanding the different types of resistors and their applications is essential for engineers and designers working with electronic circuits and devices.